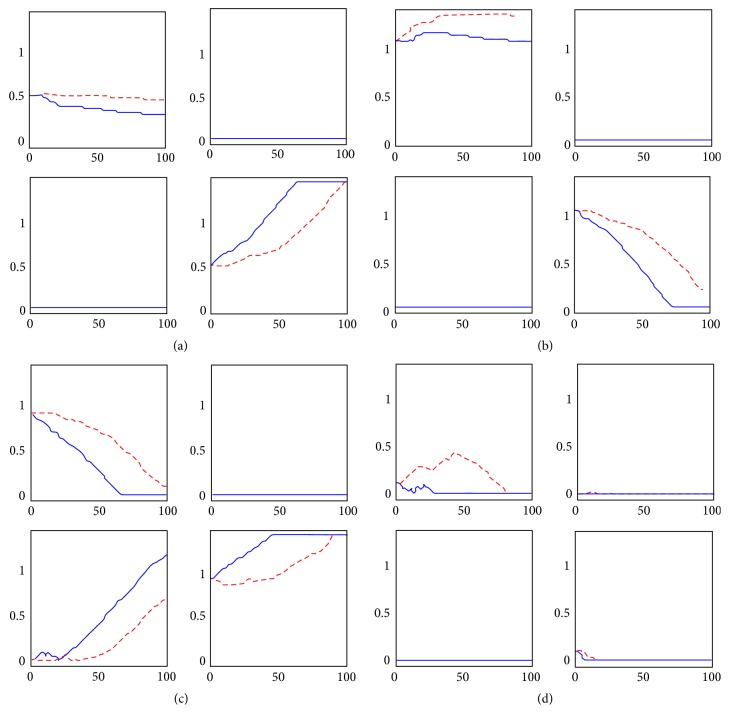
Figure 7.
Synapses update during the 100 epochs of training, red dashed line with no phasic activity of ChI, blue solid line with phasic activity of ChI. In these simulations (contrarily to Figure 3) we assumed that, before training, the input stimulus favors the third response. However, during training, the third response is punished and the fourth is rewarded. Each panel represents the submatrix W IJ (3: 4; 3: 4). Row i is post-synaptic neuron i, while column j is presynaptic neuron j. (a) W GC (3: 4; 3: 4). (b) W NC (3: 4; 3: 4). (c) W GS (3: 4; 3: 4). (d) W NS (3: 4; 3: 4). Recalling that W GC is implied in the direct pathway, the decrease of the element in the position (3,3) disfacilitates the prepotent response. Conversely, the increase of the element in the position (4,4) facilitates the desired response. Recalling that W NC is implied in the indirect pathway, the increase of the element in the position (3,3) helps suppress the prepotent response. On the contrary, the decrease of the element in the position (4,4) provides less inhibition to the desired response. Similar consideration can be made for W GS and less intuitively for W NS. It is evident from the red signals that the effect of the lack of acetylcholine induces a generally slower learning process, with synapses changing less compared to the normal case.