Figure 1.
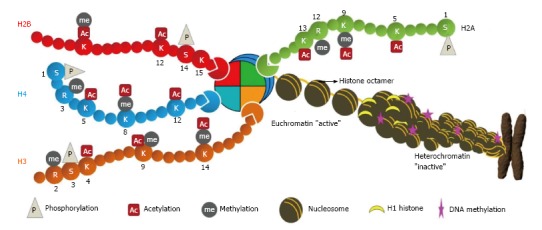
Chromatin architecture. The DNA is wrapped in two turns around histone octamers (nucleosomes) at intervals of about 200 bp along the DNA. Histones within the nucleosome (two each of H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) undergo numerous post-translational modifications at their N-terminal tail which protrudes from the nucleosome. Further folding of nucleosome with linker histone H1 creates a spiral structure, the heterochromatin leading to metaphase chromosome. These modifications directly regulate the chromatin structure and thus DNA-mediated cellular processes. The diagram indicates some modifications at specific residues: M: Methylation; A: Acetylation; P: Phosphorylation.
