Figure 2.
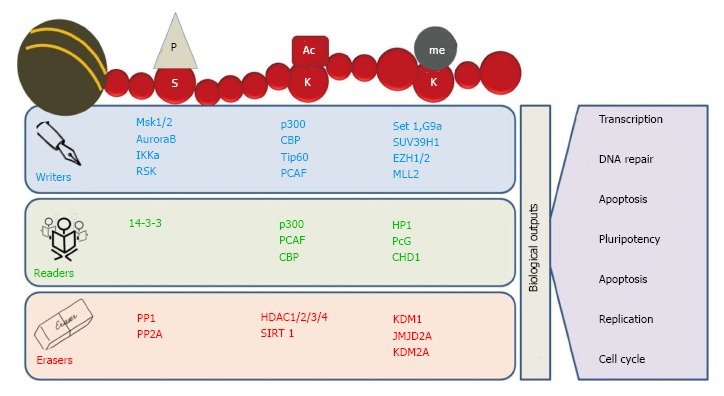
Readers, writers and erasers of chromatin marks. Histone modifications are highly dynamic in nature. The “writers” like histone acetyltransferases (HATs), histone methyltransferases (HMTs) and kinases add specific marks on specific amino acid residues on histone tails. These marks are identified by various proteins containing specific domains such as bromodomains, chromodomains and Tudor domain containing proteins called “readers”. The written marks are removed by “erasers” like histone deacetylases (HDACs), lysine demethylases (KDMs) and phosphatases. In addition, removal and identification of these post-translational modifications on histone tails regulate various biological processes, including transcription, DNA replication and DNA repair.
