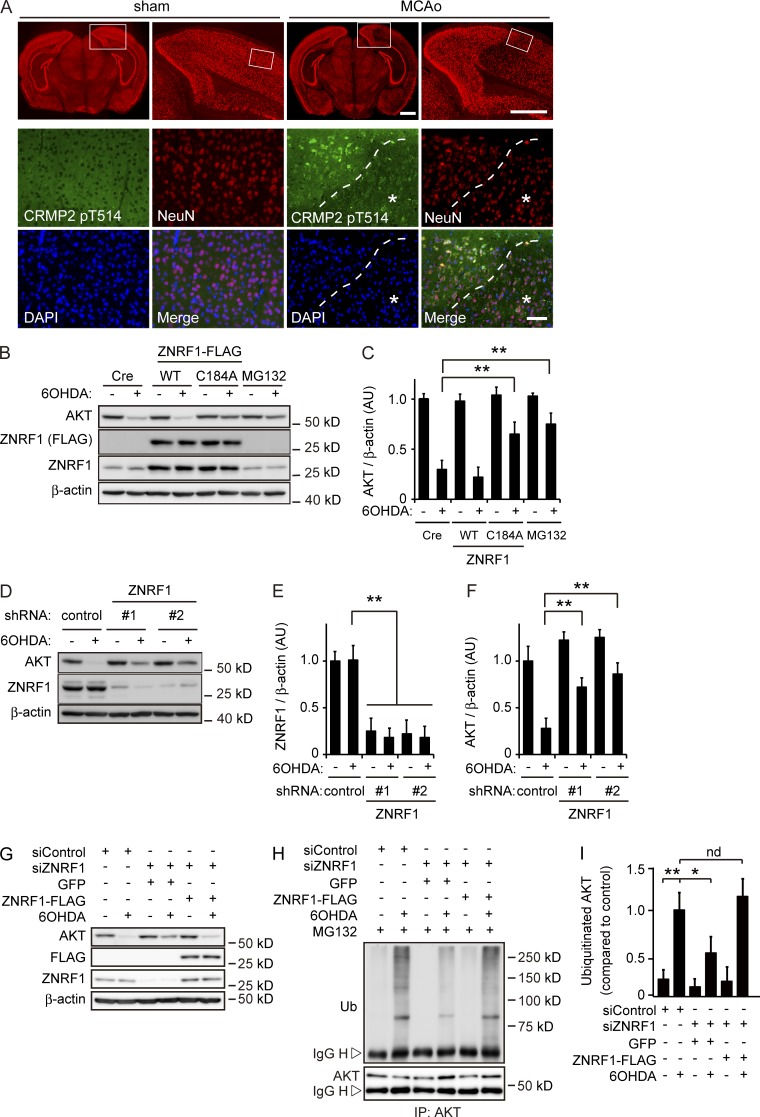
Figure 1.
ZNRF1 ubiquitin ligase activity to target AKT is induced by oxidative stress in neurons. (A) CRMP2 pT514 expression in neurons in the MCAo model. In each set of sham and MCAo panels, the top right is an enlargement of the boxed area in the top left image, and high-power images (bottom) show the boxed area in the top right image. The region with a reduced number of NeuN-positive neurons in the MCAo cortex was considered to be the infarct core (indicated by asterisks). Dashed lines indicate the border between the ischemic penumbra and infarct core. Bars: (top) 1 mm; (bottom) 50 µm. (B and C) ZNRF1 promotes UPS-mediated AKT degradation in 6OHDA-treated primary cultured cortical neurons. Representative immunoblots (B) and quantified levels for AKT normalized to β-actin relative to the control (C) are shown. (D–F) ZNRF1 down-regulation results in decreased AKT degradation. Representative immunoblots (D) and quantified levels for ZNRF1 (E) and AKT (F) normalized to β-actin relative to the control are shown. (G–I) ZNRF1 down-regulation decreases AKT ubiquitination in response to 6OHDA. Shown are representative immunoblots (G), immunoprecipitation using an anti-AKT antibody analyzed by immunoblotting (H), and quantified levels for polyubiquitinated AKT normalized to β-actin relative to the control (I). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. n = 5. Significant differences from the control (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01) were determined by a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. AU, arbitrary units; IgG H, IgG heavy chain; IgG L, IgG light chain; IP, immunoprecipitate; nd, no significant difference; Ub, ubiquitin.