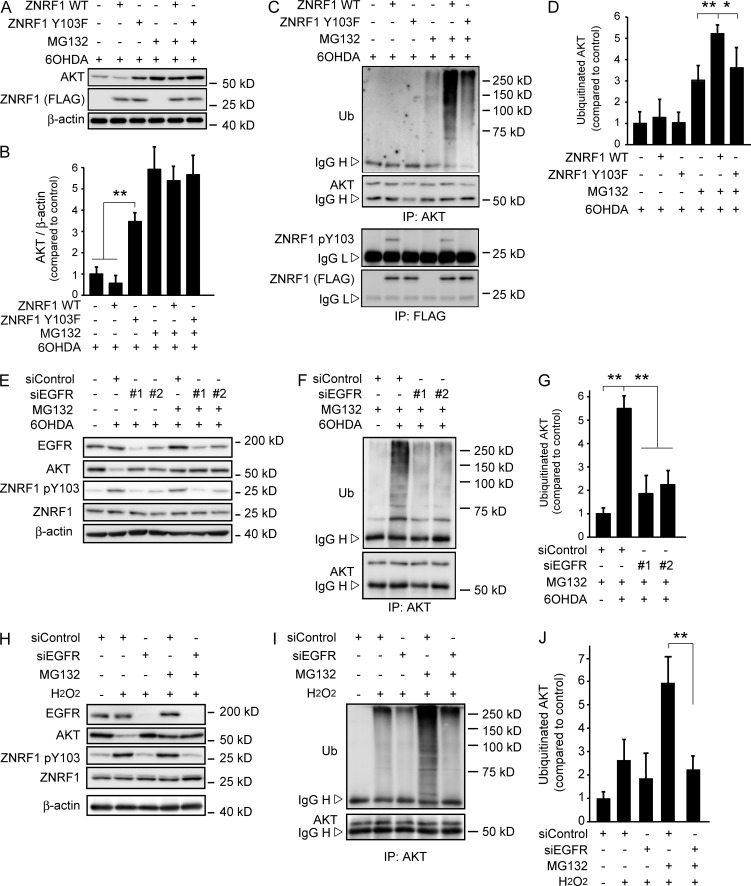
Figure 3.
Phosphorylation of ZNRF1 at Y103 by EGFR in response to oxidants induces its ubiquitin ligase activity to degrade the AKT protein. (A–D) ZNRF1 pY103 in response to 6OHDA results in the induction of ubiquitin ligase activity in cultured cortical neurons. Representative immunoblots (A) and quantified levels for AKT normalized to β-actin relative to the control (B) are shown. The immunoprecipitates using antibodies against AKT (C, top) or FLAG (C, bottom) analyzed by immunoblotting and quantified levels for polyubiquitinated AKT normalized to β-actin relative to the control (D) are shown. (E–G) EGFR down-regulation in 6OHDA-treated cultured cortical neurons results in reduced ZNRF1 pY103 levels and resultant reductions in its ubiquitin ligase activity. Shown are representative immunoblots (E), immunoprecipitates using an anti-AKT antibody analyzed by immunoblotting (F), and quantified levels for polyubiquitinated AKT normalized to β-actin relative to the control (G; labeled as +siControl/+MG132/−6OHDA). (H–J) EGFR down-regulation in H2O2-treated cultured cortical neurons results in reduced ZNRF1 pY103 levels and resultant reductions in its ubiquitin ligase activity. Shown are representative immunoblots (H). Immunoprecipitates using an anti-AKT antibody analyzed by immunoblotting (I) and quantified levels for polyubiquitinated AKT normalized to β-actin relative to the control (J; labeled as +siControl/+MG132/−H2O2) are also shown. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. n = 5. Significant differences from the control (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01) were determined by a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. IgG H, IgG heavy chain; IgG L, IgG light chain; IP, immunoprecipitate; Ub, ubiquitin.