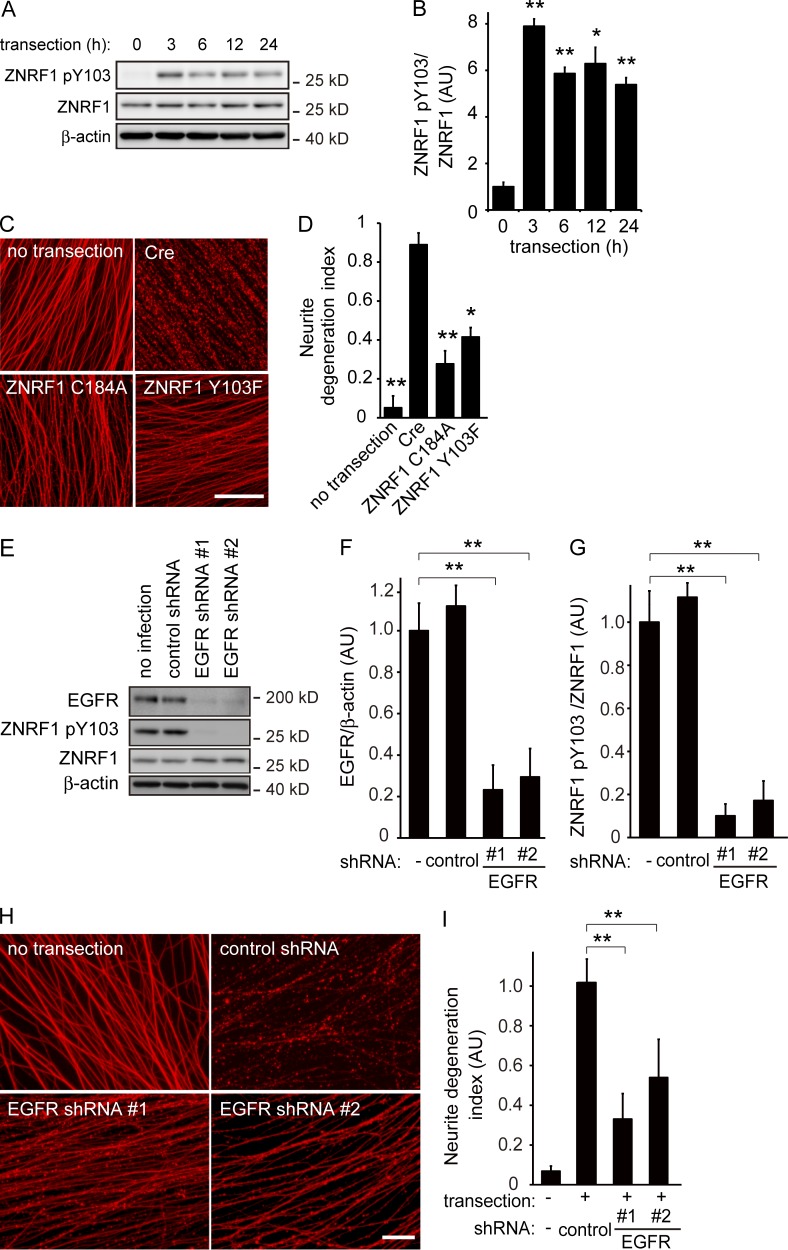
Figure 6.
Phosphorylation of ZNRF1 at Y103 by EGFR is involved in the progression of Wallerian degeneration. (A and B) ZNRF1 is phosphorylated at Y103 in neurites from cultured DRG explant neurons during Wallerian degeneration in vitro. The Wallerian degeneration of neurites was induced by removing cell bodies at 10–14 d in vitro using a pipette tip. Representative images of immunoblots at the indicated time points (A) and quantified expression levels for ZNRF1 pY103 normalized to ZNRF1 relative to the control level (before injury) are shown (B). n = 3. (C and D) The neurite protective effects induced by ZNRF1–AKT–GSK3B pathway molecules were assessed using an in vitro Wallerian degeneration model with neurites overexpressing the indicated proteins. (C) Representative photomicrographs of degenerating neurites expressing the indicated proteins 24 h after neurite transection are shown. Bar, 25 µm. (D) Neurite degeneration index values calculated for each condition at 24 h are shown. n = 5. (E–I) EGFR down-regulation decreases ZNRF1 pY103 levels and inhibits Wallerian degeneration. ZNRF1 pY103 expression levels with shRNA-mediated EGFR down-regulation were assessed by an immunoblot analysis. Representative immunoblots (E), efficiency of shRNA-mediated EGFR down-regulation (F; normalized by β-actin, relative to the no infection condition), and quantified expression levels of ZNRF1 pY103 (G; normalized by ZNRF1 relative to the no infection condition) are shown. Representative photomicrographs for the β-tubulin immunostaining of neurites are shown in H. Bar, 50 µm. Neurite degeneration index values calculated for each condition at 24 h are shown in I. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Significant differences from the control (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01) were determined by a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. AU, arbitrary units.