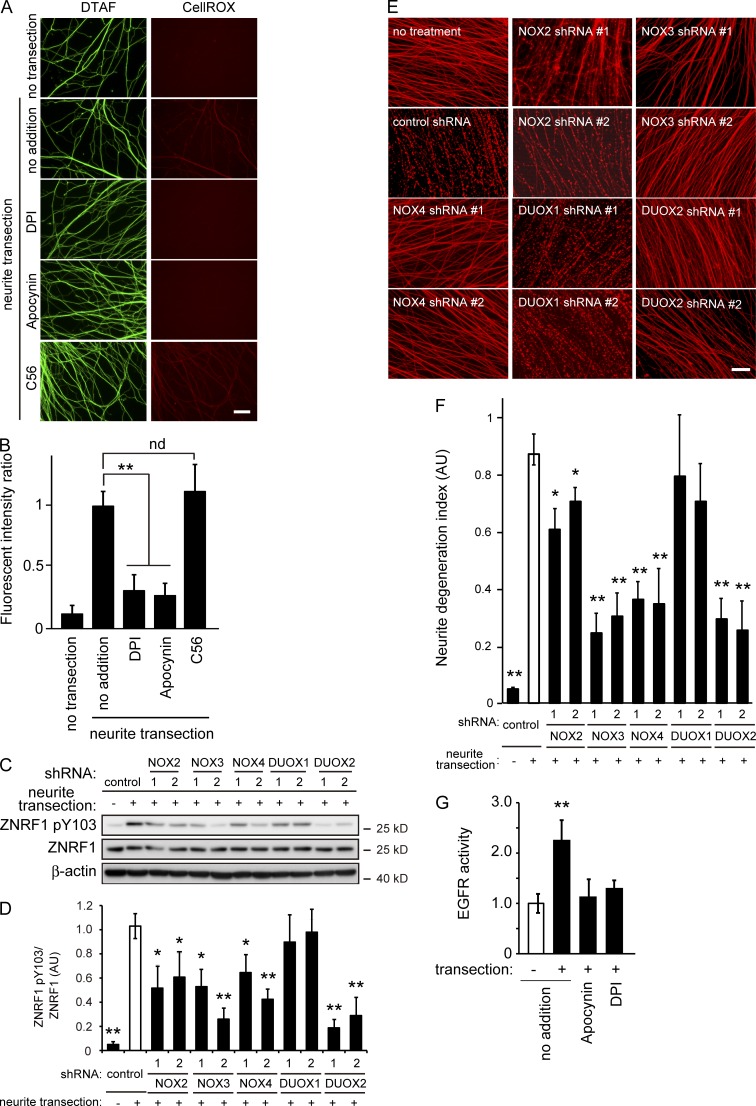
Figure 7.
Inhibition of NADPH oxidases prevents ZNRF1 phosphorylation and delays Wallerian degeneration in vitro. (A and B) NADPH oxidase inhibitors, but not C56, an EGFR inhibitor, prevent the generation of oxidative stress in degenerating neurites of cultured DRG neurons. Oxidative stress in the transected neurites of cultured DRG neurons with or without the indicated inhibitors was visualized using the fluorogenic probe CellROX deep red. The green fluorescent reagent DTAF was used for neurite staining. (A) Representative photomicrographs of the fluorescent signal in transected neurites are shown. Bar, 25 µm. (B) Quantified levels of fluorescent intensities for CellROX normalized to DTAF relative to the level in the control (labeled as “no addition, neurite transection”) are shown. Note that the generation of oxidative stress in the transected neurites in cultured DRG neurons was blocked by the NADPH oxidase inhibitors DPI and apocynin, but not the EGFR inhibitor C56. (C–F) Effects of the down-regulation of the catalytic subunits of the NADPH oxidases NOX2, 3, 4, DUOX1, and 2 were assessed using an in vitro Wallerian degeneration model with cultured DRG neurons. Representative immunoblots for ZNRF1 pY103 and ZNRF1 (C) and quantified expression levels for ZNRF1 pY103 normalized to ZNRF1 relative to the control (D; nontarget control shRNA–expressing, neurite-transected condition) are shown. (E) Representative photomicrographs for the β-tubulin immunostaining of neurites are shown. Bar, 50 µm. (F) Neurite degeneration index values calculated for each condition at 24 h are shown. (G) Up-regulation of EGFR kinase activity in neurites after transection. Immunopurified EGFR protein samples from the neurites of cultured DRG explant neurons 3 h after transection in the presence or absence of the NADPH oxidase inhibitors, apocynin and DPI, were subjected to the kinase assay. Quantified EGFR kinase activity levels in each condition relative to the control (labeled as “−transection/no addition“) are shown. Note that EGFR activity increases in neurites after injury are dependent on oxidative stress generated by NADPH oxidase activity. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. n = 5. Significant differences from the control (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01) were determined by a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. nd, no significant difference.