Fig. 4.
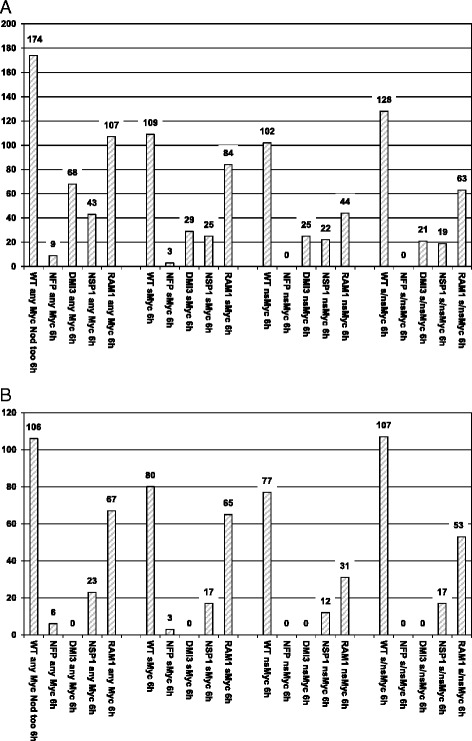
Sym-LCO related gene expression in the M. truncatula wild type and in four symbiotic mutants. a Number of genes at least 1.5-fold (p < 0.05) up-regulated in M. truncatula wild type A17 (WT), nfp-1 (NFP), dmi3 (DMI3), nsp1-1 (NSP1), and ram1-1 (RAM1) plantlet roots challenged for 6 h with 10−8 M sMyc-LCOs (sMyc), 10−7 M nsMyc-LCOs (nsMyc), or a mixture of 10−8 M sMyc- and 10−7 M nsMyc-LCOs (s/nsMyc). These genes were also activated by Nod-LCOs at this cutoff (Additional file 3: Table S3). On the left, the three Myc-LCO specific data columns are summed up, regardless of individual Myc-LCOs. Values do not add up due to an overlapping activation of transcription by different LCOs. The number of genes induced by Myc-LCOs in the wild type still activated in four symbiotic mutants are shown to the right of the wild type columns. b Genes still activated in dmi3 mutants were subtracted (Additional file 4: Table S4) to highlight CSSP-dependent effects
