Fig. 1.
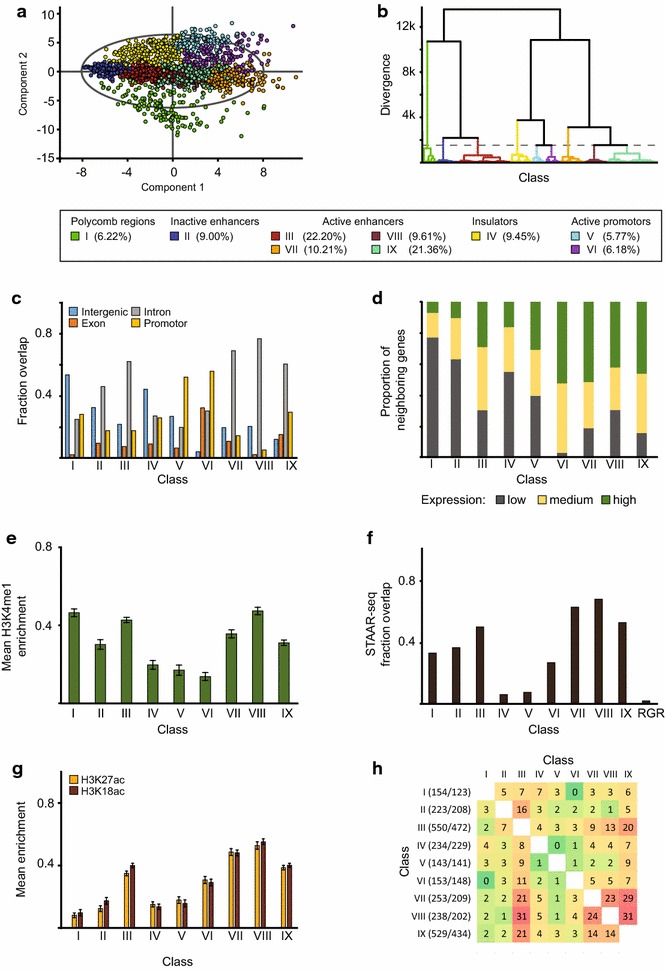
Classification of CBP binding sites and identification of promoter and enhancer classes. a Score plot of the first two components from principal component analysis (PCA) of 42 protein binding values within CBP binding sites. b Hierarchical clustering of CBP binding sites based on the four significant principal components. The dashed line indicates the cut-off used to define nine classes. These classes represent regions with a distinct combination of factors bound, and correspond to various kinds of cis-regulatory regions. The percentages of CBP binding regions from each class are given in brackets. c Fraction of CBP peaks in the nine classes overlapping different gene features. d Fraction of CBP peaks in the nine classes associated with genes divided into three levels of expression. e H3K4me1 enrichment within 500 bp around the CBP peak centres in the nine CBP classes. f Fraction of CBP regions in the nine classes and in random genomic regions (RGR) that are associated with STARR-seq enhancer peaks. g H3K27ac and H3K18ac enrichment within 500 bp around CBP peak centres in nine classes of CBP. Values were scaled so that a value of zero corresponds to the genomic mean and a value of one to the genomic maximum in e and g. Error bars represent 95 % confidence intervals. h Percentage overlap between the genes associated with each class. Each row represents the percentage of the genes associated with that class that is also associated with each of the other eight classes. Within parenthesises the number of CBP regions and number of unique genes assigned to each class
