Fig. 1.
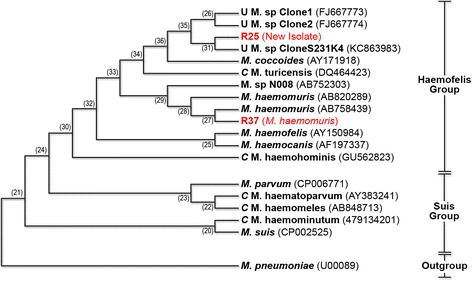
Phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences, showing the relationship between the two isolates from rats (R25 and R37) and other hemotropic mycoplasmas. GenBank® accession numbers are included. The evolutionary history was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method [32]. The optimal tree with the sum of branch length = 5,36444540 is shown. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) are shown next to the branches [34]. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Maximum Composite Likelihood method [45] and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site. The analysis involved 19 nucleotide sequences. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. There were a total of 899 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA6 [31]
