Fig. 8.
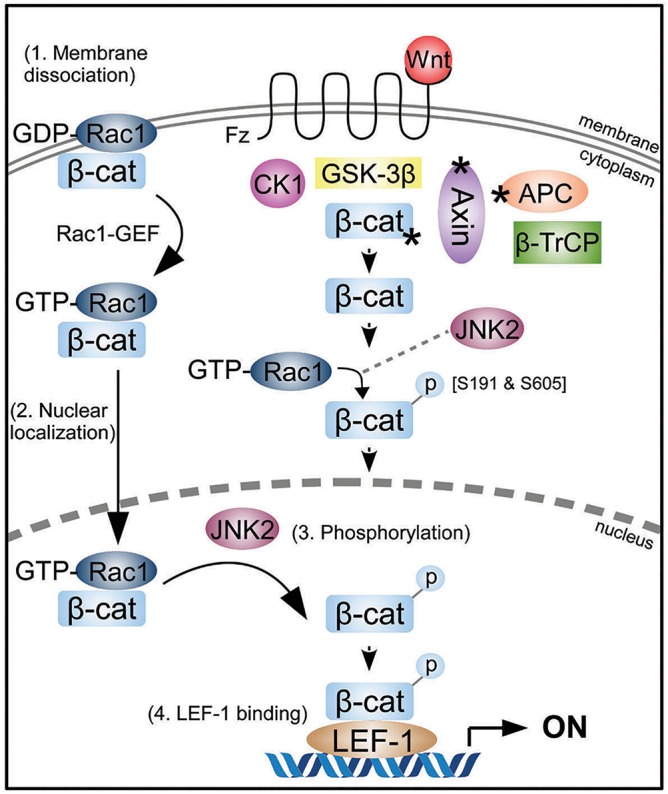
Rac1 activation and Wnt synergistically enhance β-catenin transactivation in the canonical Wnt pathway. In Wnt stimulated cells or in cancer when there are mutations in key pathway components (*Axin, APC, β-catenin) β-catenin is driven into the nuclei of cells to transactivate Wnt target genes in co-operation with LEF-1/TCF transcription factors. In addition to Wnt, active Rac1 augments the transcription of Wnt target genes through the following steps: (1) loss of β-catenin membrane retention after Rac1 activation; (2) increased nuclear localization of active Rac1–β-catenin complexes; (3) phosphorylation of β-catenin at S191 and S605 by JNK2, leading to (4) increased binding of phosphorylated β-catenin to the transcription factor LEF-1 and enhanced transactivation. It is possible that phosphorylation of β-catenin at S191 and S605 could occur in either nucleus or cytoplasm.
