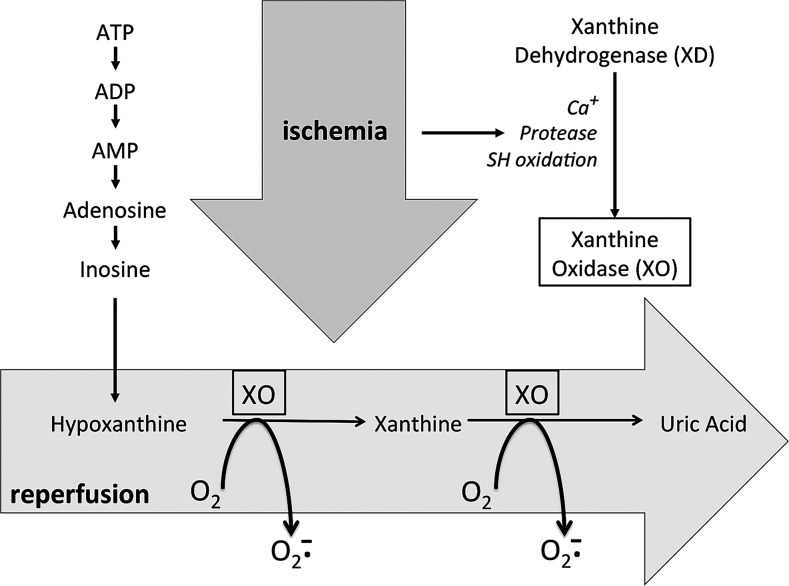
FIG. 4.
Role of XO in ischemia–reperfusion-induced oxidative stress. During ischemia, ATP causes accumulation of its catabolite, hypoxanthine. Ischemia also induces conversion of XD into XO. During reperfusion, with oxygen available again, hypoxanthine is oxidized to uric acid, while molecular oxygen is concomitantly reduced to O2−. Scheme derived from (89).