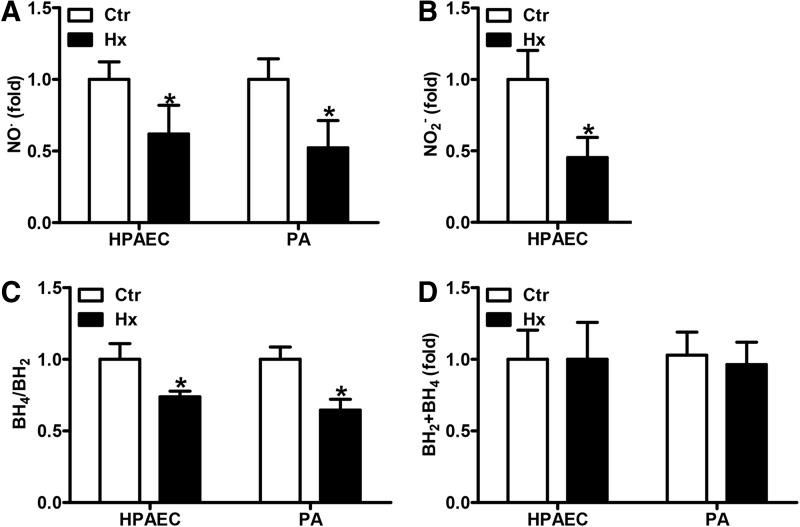
FIG. 1.
Hypoxia decreases NO availability. (A–D) HPAECs or isolated murine PAs were incubated in hypoxic (1% oxygen, Hx) or normoxic conditions (Ctr) for 24 h. (A) NO levels were measured by EPR using iron(2+)–diethyldithiocarbamic acid [Fe(2+)(DETC)] complex as an NO radical-specific spin probe. Normoxic levels were set equal to 1 [n = 4; *p < 0.05, (1−β) ≥0.897 vs. Ctr]. (B) Nitrite levels were determined in the supernatant of HPAECs by HPLC. Normoxic levels were set equal to 1 [n = 3; *p < 0.05, (1−β) ≥0.969 vs. Ctr). (C) BH4 and BH2 levels were measured in cell and tissue lysates by HPLC. Normoxic levels were set equal to 1 [n = 5; *p < 0.05, (1−β) ≥0.999 vs. Ctr]. (D) The sum of BH4 and BH2 levels in HPAECs and PAs was calculated. BH2, dihydrobiopterin; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; EPR, electron paramagnetic resonance; HPAEC, Human pulmonary artery endothelial cells; HPLC, high-pressure liquid chromatography; NO, nitric oxide; PAs, pulmonary arteries.