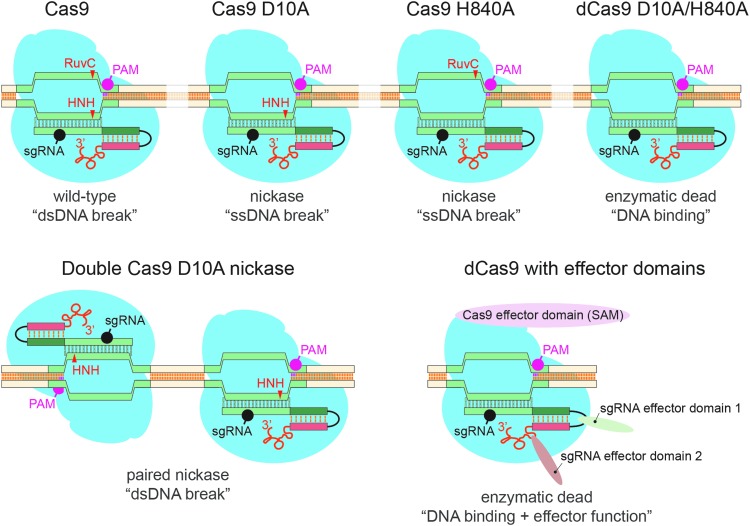
FIG. 1.
Available Cas9 species and their applications. Highlighted are the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM), the two Cas9 nuclease domains, RuvC and HNH, and the DNA position (arrowhead) on which they act as well as the position of the single-guide RNA (sgRNA). Mediated by the two nuclease domains, the wild-type enzyme generates a DNA double-strand break. Mutating a single nuclease domain, to either D10A or H840A, will result in a nickase enzyme that is only able to nick DNA at the sgRNA-targeted site. Nickase enzymes can be used in a paired manner to improve specificity and reduce off-target effects. The mutation of both nuclease domains results in a catalytically “dead” (dCas9) enzyme that retains RNA-guided DNA binding capacity. Combining dCas9 with either Cas9-linked or sgRNA-linked effector domains can be used for transcriptional activation, repression, or genomic visualization.