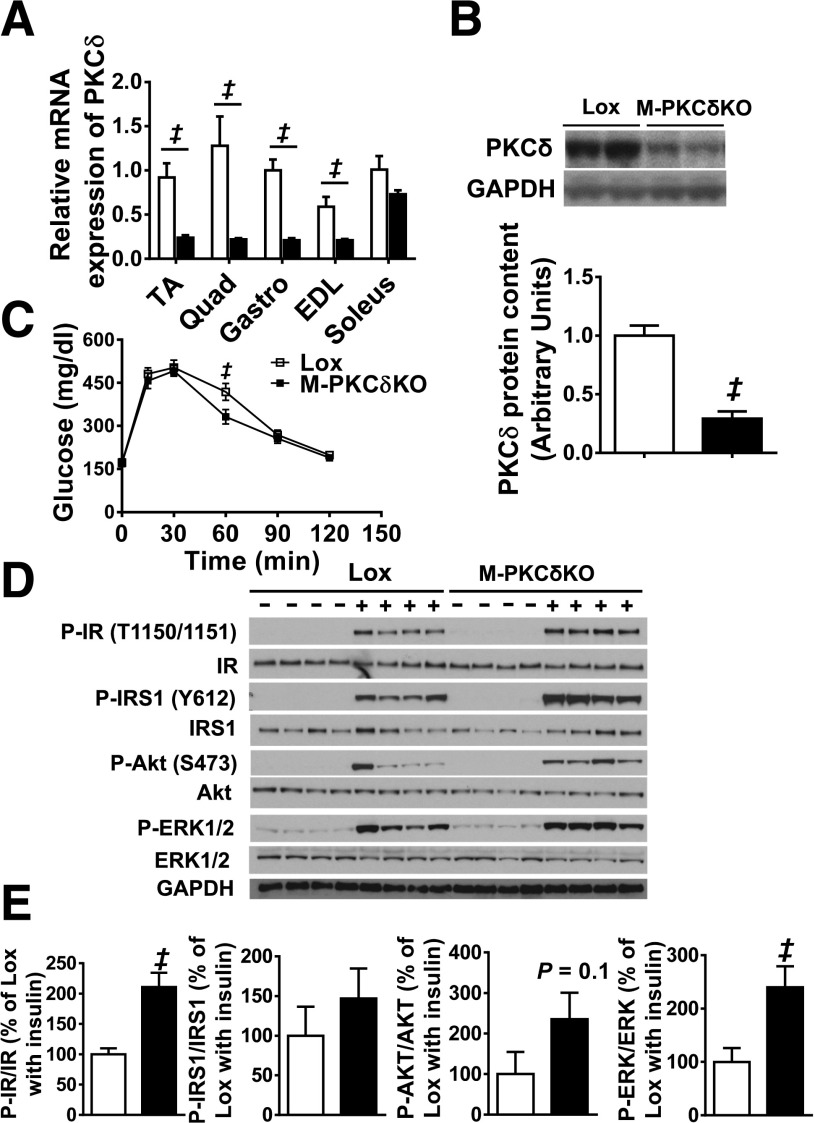
Figure 2.
Glucose tolerance and muscle insulin signaling are normal in muscle-specific PKCδ knockout mice at 10 weeks of age. A: PKCδ mRNA expression in TA, quadriceps (Quad), gastrocnemius (Gastro), EDL, and soleus muscles from Lox and M-PKCδKO mice. B: Representative Western blots and densitometric quantification of PKCδ in the purified TA muscle fibers of Lox and M-PKCδKO mice with quantification below. C: Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance tests were performed in Lox and M-PKCδKO mice. D: Western blot analysis of insulin signaling pathway in skeletal muscle of Lox and M-PKCδKO mice after insulin injection (20 units/kg body wt i.v.). E: Densitometric analysis of IR, IRS-1, AKT, and EKR phosphorylation from D after insulin stimulation. □, Lox mice; ■, M-PKCδKO mice. Data are means ± SEM. n = 6–8 per group in panels A–C, and n = 4 per group for panels D and E. ‡P < 0.05 by Student t test.