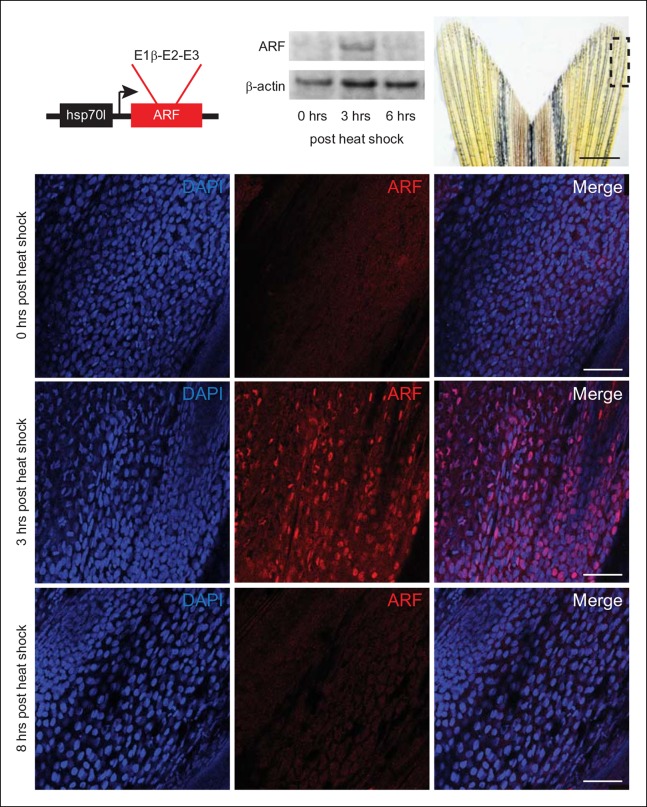
Figure 3. Expression of the mammalian tumor suppressor ARF in zebrafish driven by heat shock promoter. .
In vivo analysis of transgenic zebrafish expressing human ARF under the control of an inducible heat shock promoter, Tg (hsp70l:ARF) (hs:ARF). Schematic of the hs:ARF transgene (top left). The ARF cassette included in the transgene is a cDNA that consists of human exons 1b, 2, and 3 of CDKN2A. Representative Western blot of 3 replicates of ARF before (0 hr) and 3 and 6 hr post heat shock induction of ARF expression (top middle). Portion of fin shown for analysis of expression in vivo (top right; dashed box). Scale bar: 1 mm. Immunostaining (sagittal confocal images) for ARF in adult hs:ARF zebrafish fins at 0, 3, and 8 hr after a single, hour long, 37°C heat shock (bottom). Scale bars: 50 μm. ARF expression is maximal at 3 hr post heat shock, and it is undetectable by 8 hr post heat shock. Figure supplement 1 shows in vitro assays.