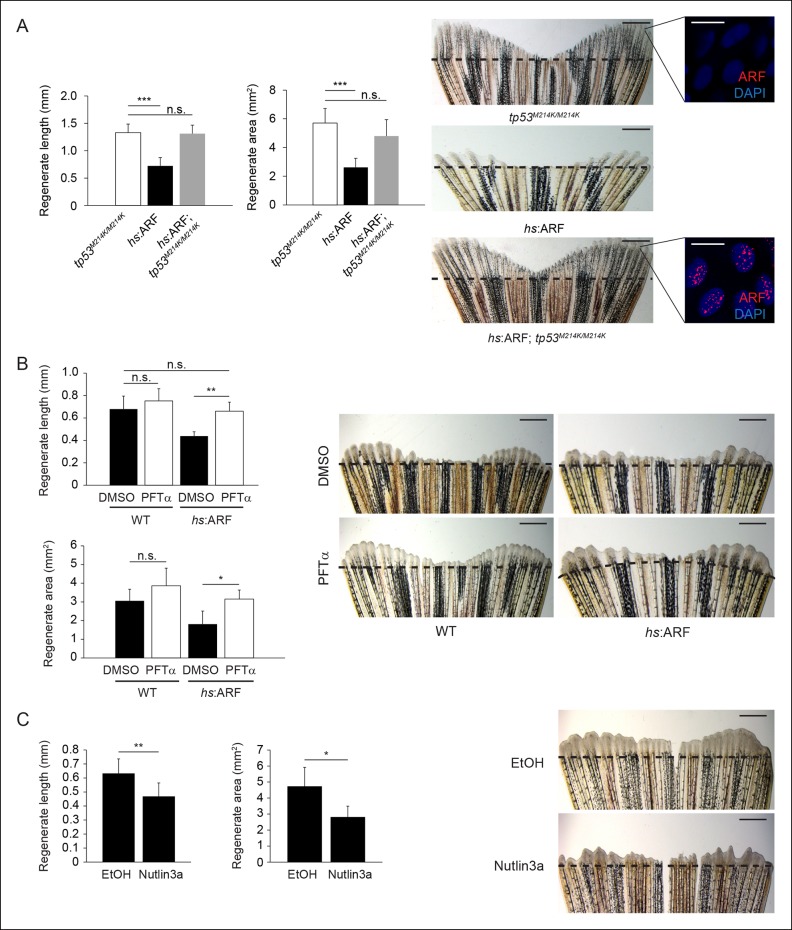
Figure 5. Human ARF functions through the Tp53 pathway in fish to suppress regeneration.
(A) Quantification of regenerate length and area at 6 dpa in tp53M214K/M214K, hs:ARF, and hs:ARF; tp53M214K/M214K fins exposed to the heat shock regimen as in Figure 4 (left; N = 30 fins). Representative images of fin regeneration at 6 dpa in tp53M214K/M214K, hs:ARF, and hs:ARF; tp53M214K/M214K fins exposed to heat shock (right). Scale bars: 1 mm. Immunostaining (sagittal confocal images) for ARF in tp53M214K/M214K and hs:ARF; tp53M214K/M214K fins 3 hr after a single heat shock (right inset). Scale bars: 10 μm. Fin regeneration proceeds equally well in tp53M214K/M214K and hs:ARF; tp53M214K/M214K fins exposed to heat shock, but fin regeneration inhibition is observed in hs:ARF fins exposed to heat shock. (B) Quantification of regenerate length and area at 4 dpa in wild type (WT) and hs:ARF fins exposed to heat shock and 5 μM pifithrin-α(PFTα) or 0.1% Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (vehicle) (left; N = 8 fins, p<0.01). Representative images of fin regeneration at 4 dpa in WT and hs:ARF fins exposed to heat shock and 5 μM PFTα or 0.1% DMSO (right). Scale bars: 0.5 mm. Inhibition of Tp53 activity with PFTα rescues regeneration suppression by ARF. (C) Quantification of regenerate length and area at 4 dpa in WT fins exposed to 5 μM nutlin3a or Ethanol (EtOH) (vehicle) (left; N = 8 fins, p<0.01). Representative images of fin regeneration at 4 dpa in WT fins exposed to 5 μM nutlin3a or EtOH (right). Scale bars: 0.5 mm. Inhibition of Mdm2 with nutlin3a phenocopies ARF expression by suppressing fin regeneration. The dashed lines represent amputation planes. Results are shown as mean ± standard deviation. n.s.: not significant.