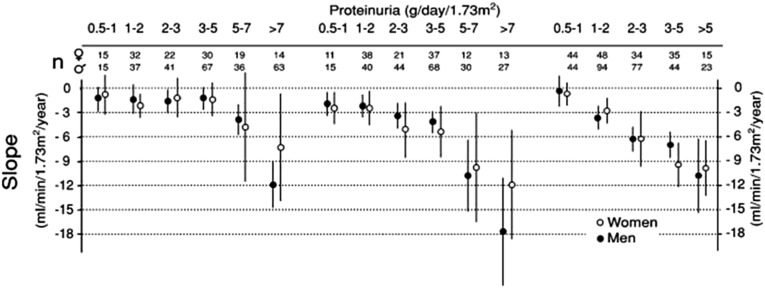
Figure 1.
Relation between time-average proteinuria and the rate of renal function decline in MN, FSGS, and IgA nephropathy. Declines in renal function are associated with higher levels of sustained proteinuria in patients with MN (where a decline is observed at levels of sustained proteinuria >5 g/d) than in patients with FSGS (where a decline in renal function is observed with sustained proteinuria around 2–3 g/d) or patients with IgA nephropathy (where a decline in renal function is observed with sustained proteinuria >1 g/d). Thus, the severity of proteinuria alone does not fully explain the rate of loss of renal function, and other disease–specific factors likely play a role. Black circles, men; white circles, women. Reprinted from ref. 22, with permission.