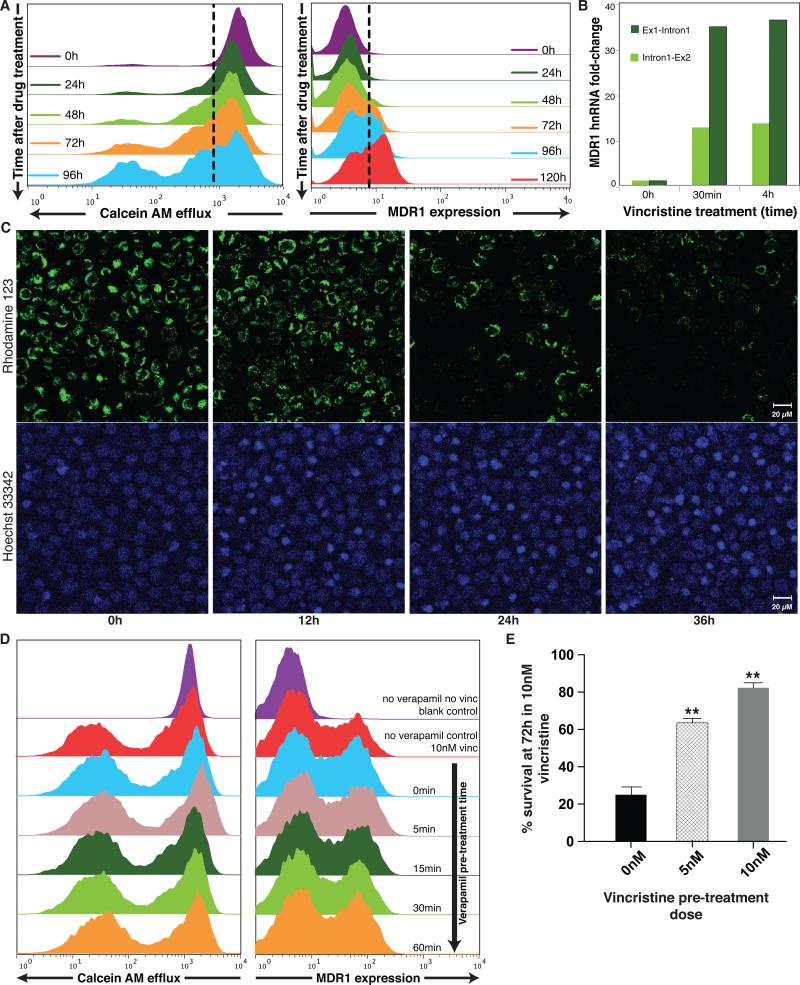
Figure 2. Chemotherapy induces expression of the MDR1 protein and the MDR phenotype in HL60 cell population.
(A) Flow cytometry measurements of surface MDR1 (immunostaining) and cell efflux capacity (fluorescent dye ejection) at the population level reveal the kinetics for the appearance of the MDR1High and the MDRHigh/effluxHigh subpopulation following vincristine treatment. (B) Quantitative (real-time) RT-PCR (qPCR) uisng primers targeting the first two exon-intron junctions of MDR1 to measure hnRNA as marker of ongoing transcription. Bar height indicate average (n = 2) of one experiment representative of two independent experiments. Standard deviations of all shown qPCR Ct-values were < 0.7 (C) Cell-individual induction of the MDR phenotype by vincristine. Cells loaded with the fluorescent dye Rhodamine123 (green) as marker of efflux capacity and stained with a DNA dye (Hoechst 33342, blue) as cell indicator and to monitor cell death, were treated with VINC (10nM) time t = 0h and followed by video microscopy under incubator conditions for 36 h. Scale bar = 20μm. (Supplementary Movies 1 and 2 for longitudinal tracking of the individual cells and Supplementary Fig. S8). Snapshots at the indicated times are shown. Disappearance of the green fluorescent dye in the viable cells indicates cell autonomous induction of the MDR phenotype. Nuclear condensation in the Hoechst 33342 stain reveals apoptotic cells. As dying cells will eventually release the dye, we quantified only live cells for dye elimination. After 48h monitoring of a typical time-course, 63 % of the live cells treated with VINC exhibited elimination of the dye, representing the switch to the effluxHigh phenotype compared to 16 % of untreated cells (n=80 cells counted). (D) Saturating doses of verapamil, an inhibitor of MDR1-mediated transport, given at varying times prior to vincristine treatment as indicated, does not alter the induction of MDR1 after 72h of treatment with vincristine. (E) HL60 cells previously exposed for 48h to the indicated doses (5 nM, 10nM) of vincristine exhibited improved survival compared to naïve cells when challenged with 10nM vincristine for 72h. Error bar, standard deviation (n= 3), ** p< 0.01, t-test)