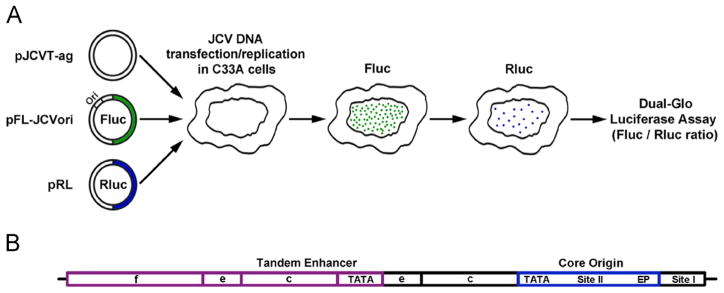
Fig. 1.
Diagrams of the luciferase based JCV replication assay and the Mad-1 NCCR. A. On the left are depictions of three plasmid types used in the assay. They include a plasmid encoding JCV T-ag (pJCVT-ag), a plasmid containing both the JCV origin of replication and the firefly Fluc gene (pFL-JCVori) and a plasmid encoding Renilla luciferase (pRL). These plasmids are transfected into human cell lines where T-ag dependent replication takes place. Following an adequate time (e.g., 48 or 72 h) the amount of light released by the firefly and renilla luciferases is measured using a luminometer. B. A diagram of the tandemly duplicated regulatory sequences adjacent to the JCV origin of replication in the Mad-1 strain (Frisque, 1983). Individual regions within the NCCR are indicated; they include the core origin (containing the central Site II region and flanking early palindrome (EP) and TATA regions), Site I and subdomains within the enhancers.