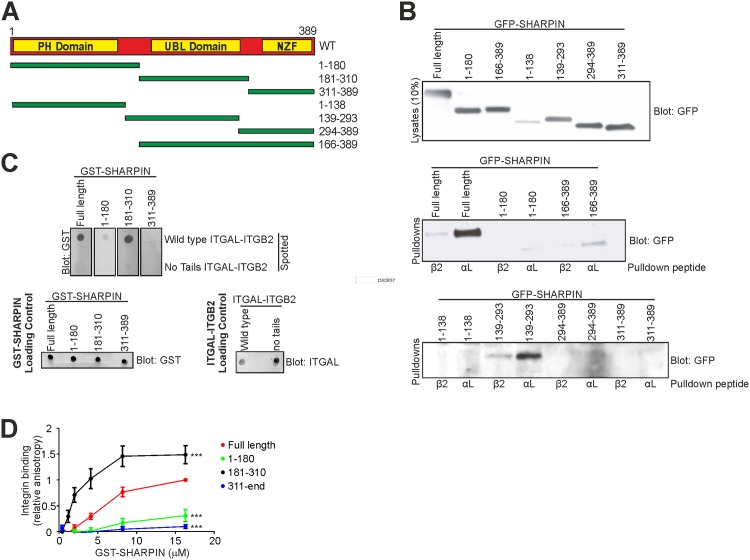
Fig 1. The UBL domain of SHARPIN mediates binding to integrin.
(A) Schematic representation of SHARPIN with its functional domains and the SHARPIN fragments used in this study. (B) Pull-down experiments to determine the interaction between GFP-SHARPIN (full-length or fragments) and peptides corresponding to the cytoplasmic domain of ITGAL and ITGB2. (C) Far-Western analysis of GST-SHARPIN (full-length or fragments) binding to full-length ITGAL-ITGB2 or ITGAL-ITGB2 lacking both cytoplasmic tails. Loading controls for GST-SHARPIN (full-length or fragments) and both ITGAL-ITGB2s are shown. (D) Fluorescence polarization-based titration of GST-SHARPIN (full-length or fragments) binding to an integrin peptide corresponding to the conserved domain within the cytoplasmic tail of ITGA2. Average normalized binding curves are shown (mean ± s.e.m. ***: p<0.001).