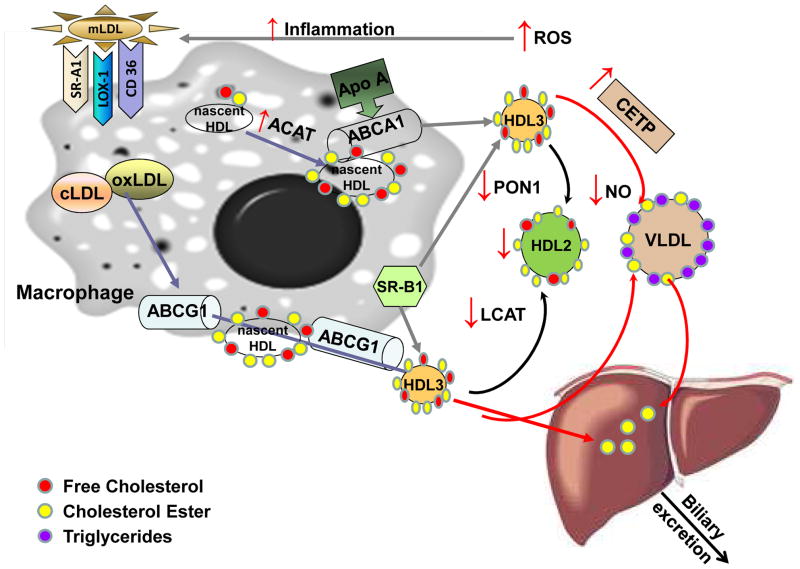
Figure 2. Reverse cholesterol transport in chronic kidney disease.
CKD alters lipoprotein composition through multiple mechanisms, not all of which are understood. Loss of protein is thought to contribute, as is augmented production of ROS. Inflammation and ROS may lead to accumulation of modified LDL (mLDL), such as highly oxidized LDL (oxLDL) or carbamylated LDL (cLDL). Internalization of modified LDL in macrophages occurs via the major scavenger receptors (CD36, SRA-1, LOX1) and contributes to foam cell formation. The presence of mLDL enhances expression of the ABCG1 transporter. In CKD, an elevated level of ACAT-2 facilitates formation and domination of cholesterol esters. Removal of free cholesterol from macrophages proceeds via SR-B1, which contributes to HDL formation through both ABC transporters (ABC) A1 and ABCG1. Cholesterol and phospholipids are eliminated through formation of nascent HDL from circulating Apo-AI. ABCA1 and ABCG1 show additive activity in promoting macrophage reverse cholesterol transport. Nascent HDL is generated when Apo-AI interacts with ABCA1. Uptake of free cholesterol and its conversion to cholesterol ester is mediated by LCAT and results in transformation of HDL3 to HDL2. In kidney disease, conversion of HDL3 to HDL2 is impaired because of LCAT deficiency. CETP mediates transfer of cholesterol ester from HDL to triglyceride rich lipoproteins - VLDL. In CKD, increased activity of CETP is detected, which contributes to low plasma HDL. In uremic patients on maintenance hemodialysis, cholesterol efflux capacity of HDL is markedly reduced when compared to HDL from healthy subjects. Moreover, anti-oxidative and antiinflammatory functions of HDL are impaired due to reduced activity of PON1. HDL from CKD patients loses its vasoprotective properties, inhibiting NO production and increasing vascular cell adhesion Oxidative modifications of HDL limit the ability of HDL to bind to SR-B1 to unload esterified cholesterol to the liver.
Abbreviations: ABCA1 and G1, ATP-binding cassette sub-family A1 and G1 members; ACAT, acyl coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase; apoA-I; apolipoprotein A-I; CETP, cholesteryl ester transfer protein;; HDL, high density lipoprotein; LCAT, lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase; LOX1, lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor 1; NO, nitric oxide; PON1, serum paraoxonase/arylesterase 1; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SRA1/B1, scavenger receptor class A member 1/class B member 1; VLDL, very low density lipoprotein.