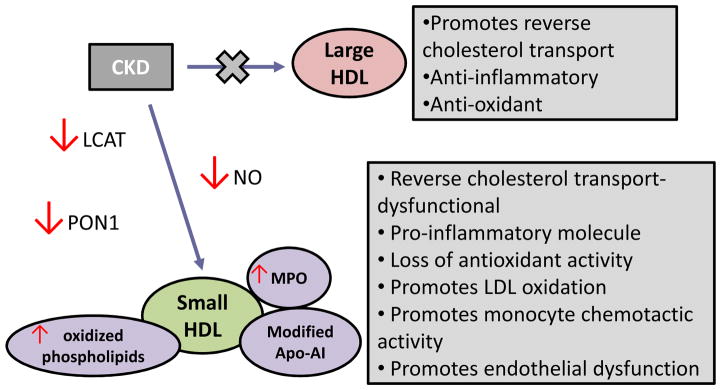
Figure 3. Changes in HDL functions mediated by CKD.
Small dense HDL particles dominate in individuals with CKD. Chronic pro-inflammatory conditions activate macrophages, releasing myeloperoxidase (MPO). MPO-derived oxidants modify HDL, which impairs the functioning of HDL-associated enzymes, such as paraoxonase 1 (PON1), nitric oxide (NO) synthase and lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT). These enzymes are essential for anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and vasoprotective properties of unmodified HDL.