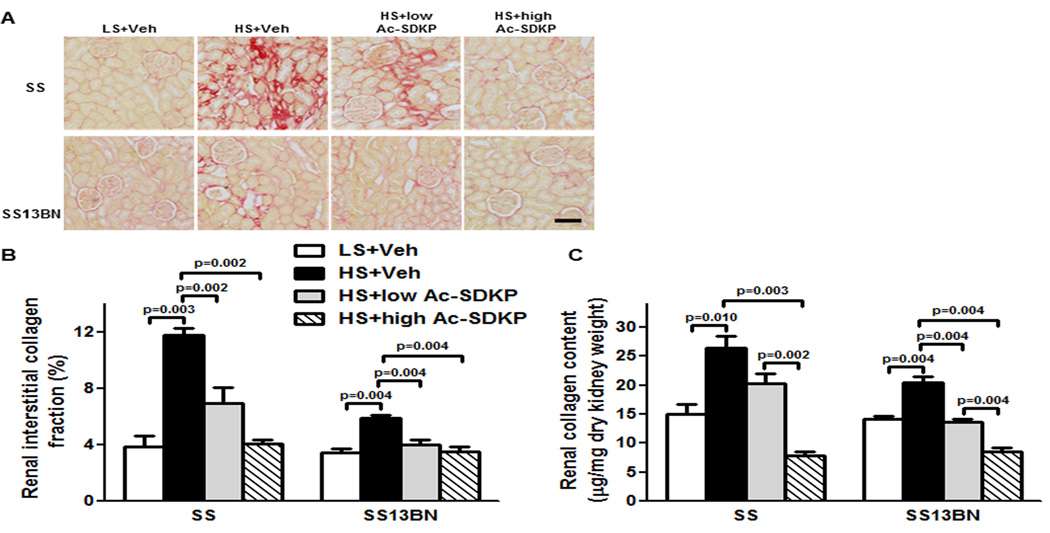
Figure 4. Effect of Ac-SDKP on renal interstitial fibrosis and collagen content.
(A) Representative images of renal interstitial fibrosis. Red color indicates collagen deposition revealed by picrosirius staining. Shown are images captured using ×20 microscope objective. Scale bar = 100 µm. (B) Quantitative data analysis. In Dahl salt-sensitive (SS) and consomic SS13BN rats, low or high dose of Ac-SDKP significantly prevented HS-induced renal interstitial collagen deposition. Data are calculated as a percentage of the fibrotic area and expressed as mean ± SEM. N=6–7 in each group. (C) Quantitative analysis of total renal collagen content determined by hydroxyproline assay. In SS and consomic SS13BN rats, HS diet significantly increased renal collagen content compared to LS diet. In SS and SS13BN rats, Ac-SDKP significantly decreased HS-induced renal collagen content. Greater decrease was observed with high Ac-SDKP compared to low Ac-SDKP in both strains. Data are expressed as a microgram of collagen per milligram of dry kidney weight and expressed as mean ± SEM. N=6–7 in each group.