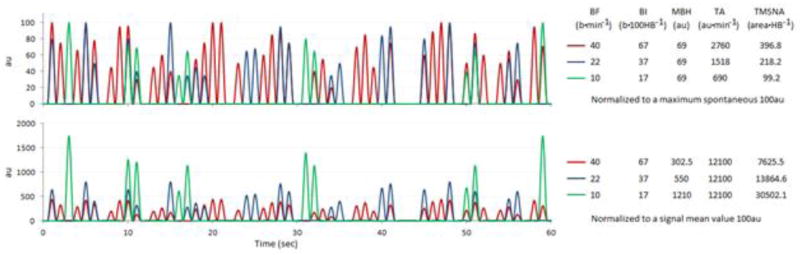
Figure 6. Comparative simulated tracings of nerve traffic normalized by maximum spontaneous burst and mean signal strength.
The top tracing shows each line having a different burst frequency (BF) but all lines have the same heart rate (HR). The simulated data are normalized to the highest burst given a value of 100au. The bottom tracing shows the same simulated data normalized to a mean signal strength of 100au. A conclusion that would be drawn from the top signals is that in a subject in which BF or BI is elevated, so are TA and TMSNA in a directly proportional manner. An alternative conclusion would be drawn from the bottom tracings in which BF and BI are the same as the top tracing, but TA shows all subjects being equal and TMSNA would conclude that the subject with the lowest bursting frequency has the highest activity. Simulated data such as these are helpful for illustrating the point that the method of signal normalization is extremely important for comparing data between subjects.