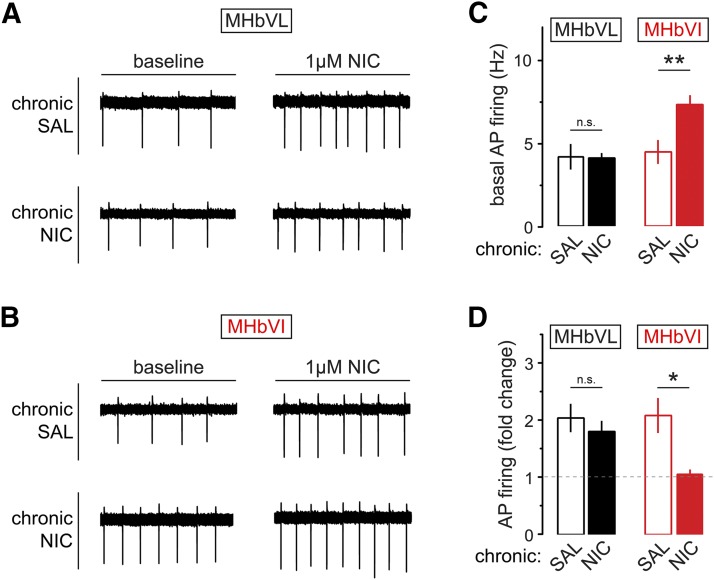
Fig. 7.
Excitability changes in MHb neurons from mice exposed to chronic nicotine or saline. (A) Baseline and nicotine-elicited changes in MHbVL neurons after chronic nicotine (NIC) treatment. Representative cell-attached firing traces for MHbVL neurons showing the typical change in firing are shown for the four indicated conditions [chronic saline (SAL), baseline; chronic SAL, 1 μM nicotine; chronic NIC, baseline; chronic NIC, 1 μM nicotine]. (B) Baseline and nicotine-elicited changes in MHbVI neurons after chronic NIC treatment. Representative cell-attached firing traces for MHbVI neurons showing the typical change in firing are shown for the four indicated conditions (chronic SAL, baseline; chronic SAL, 1 μM nicotine; chronic NIC, baseline; chronic NIC, 1 μM nicotine). (C) Summary bar graph showing mean action potential firing rate at baseline for MHbVL and MHbVI neurons from mice treated with chronic SAL or chronic NIC; **p < 0.01 (unpaired t test). (D) Summary bar graph showing mean fold change in action potential firing for nicotine-exposed (1 μM in bath for 15 minutes) MHbVL and MHbVI neurons from mice treated with chronic SAL or chronic NIC; *p < 0.05 (unpaired t test).