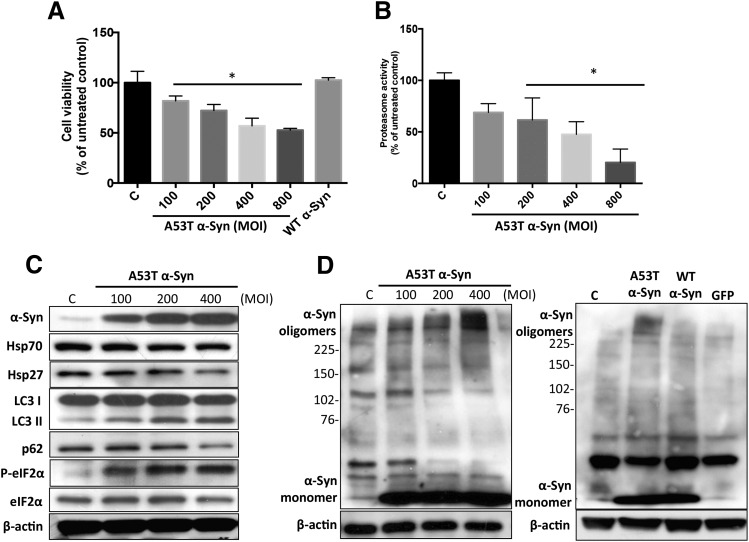
Fig. 4.
Overexpression of human mutant A53T α-Syn induced protein handling changes and toxicity in 5Y cells. (A) One day after seeding, cells were transduced with mutant A53T α-Syn (MOI from 100 to 800 plaque-forming units/cell) and WT α-Syn (MOI 400 plaque-forming units/cell) for 72 hours. Cell viability was then determined by the MTT assay. (B) Overexpression of A53T α-Syn inhibited intracellular 20/26S proteasomal activity (chymotrypsin-like active site) in a dose-dependent manner. (C) Hsp70 and Hsp27 protein levels and induction of the ER stress response and autophagy following transduction with A53T α-Syn. (D) MOI-dependent increase in higher molecular weight α-Syn oligomers was detected 72 hours after transduction with A53T α-Syn, but not WT α-Syn, and green fluorescent protein (GFP) adenovirus vector control (MOI 400 plaque-forming units/cell). β-Actin was included as a loading control. A representative blot from three separate experiments is shown for each figure. Values in (A) and (B) are presented as the mean ± S.D. (n = 3); *P < 0.05 is considered significant to control group (one-way analysis of variance using Dunnett’s multiple comparison test). P-eIF2α, phosphorylated eIF2α; MOI, multiplicity of infection.