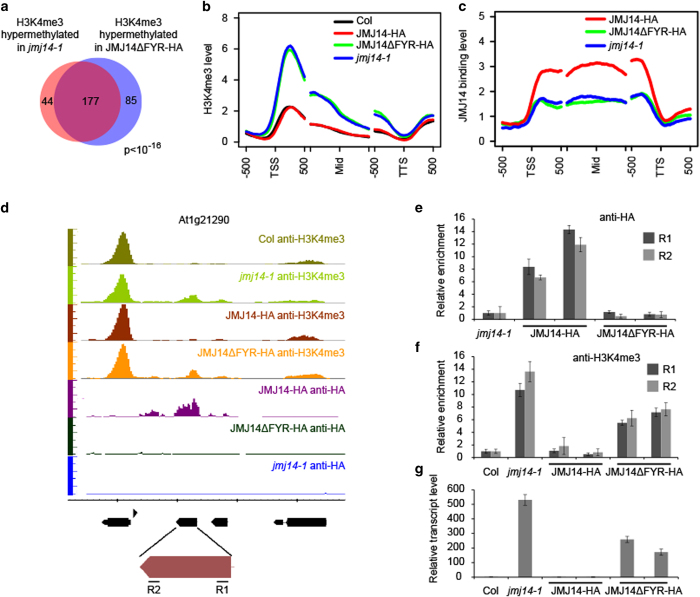
Figure 2.
JMJ14 (Jumonji C (JmjC) domain-containing protein 14) lost its targets on chromosome in the absent of FYR (FYRN+FYRC) domain. (a) The target genes with twofold increase of H3K4me3 in JMJ14ΔFYR-HA jmj14-1 transgenic plants are significantly overlapped with those in jmj14-1. (b) The H3K4me3 pattern in Columbia (Col), JMJ14-HA jmj14-1, JMJ14ΔFYR-HA jmj14-1, and jmj14-1 plants. TSS, Mid and TTS refers to transcription start site, middle of gene, and transcription termination site, respectively. Genes used for analysis were the common 177 hypermethylated genes of jmj14-1 and JMJ14ΔFYR-HA jmj14-1. (c) The JMJ14 binding level on the direct target genes of JMJ14 in JMJ14-HA jmj14-1, JMJ14ΔFYR-HA jmj14-1, and jmj14-1 plants. The tag counts were normalized in each bin according to the total number of reads. (d) The anti-HA and anti-H3K4me3 chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) results for At1g21290 locus on genome browser. (e) The anti-HA ChIP-qPCR validation for At1g21290 locus. (f) The anti-H3K4me3 ChIP-qPCR validation for At1g21290 locus. (g) Detection of At1g21290 transcripts by RT-quantitative PCR. Two independent lines of each transgenic plants were used in the qPCR. R1 and R2 indicate the 5′ and 3′ regions of the gene showed in d.