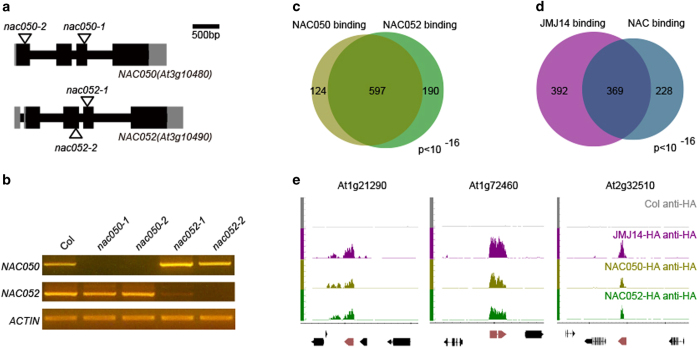
Figure 4.
NAC050 and NAC052 share common targets in direct binding with JMJ14 (Jumonji C (JmjC) domain-containing protein 14). (a) Gene structure of NAC050 and NAC052 and the T-DNA insertion sites of nac050 and nac052 mutants. Black bars, gray bars and black lines indicate coding exons, UTRs and introns, respectively. T-DNA insertions are indicated by triangles. Scale bar, 500 bp. (b) Detection of full-length CDS of NAC050 and NAC052 in the nac050 and nac052 mutants. Actin was used as an internal control. (c) The targets of NAC050 and NAC052, identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq), are significantly overlapped. (d) Nearly half of JMJ14’s targets are co-localized by both NAC050 and NAC052. (e) Three target genes showed co-localized ChIP-seq signal of JMJ14, NAC050, and NAC052 on genome browser. JMJ14-HA, NAC050-HA, and NAC052-HA indicates the PJMJ14::JMJ14-HA jmj14-1, PNAC050::NAC050-HA nac050-1, and PNAC052::NAC052-HA nac052-2 transgenic lines, respectively.