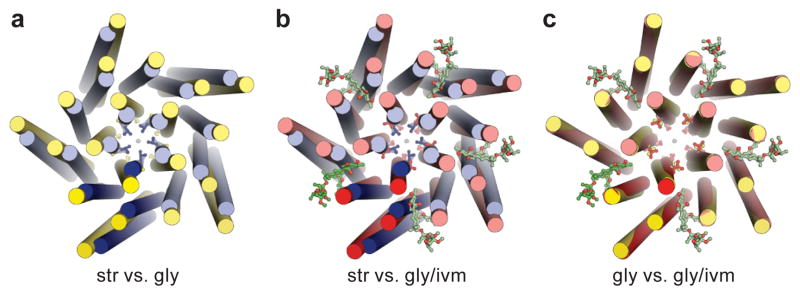
Figure 6. Overall conformational changes of the TMD.
Str-, gly- and gly/ivm-bound states are in blue, yellow and red, respectively. Comparison between str- and gly-GlyR (a), str- and gly/ivm-GlyR (b), gly- and gly/ivm-GlyR (c), viewed from the extracellular side. Side chains of −2′Pro and 9′Leu are shown in sticks to denote the change of pore sizes. In going from the str- to the gly-bound form, the TMD of each individual subunit undergoes a counter-clockwise outward rotation, enlarging the pore size by ‘pulling’ the side chains of 9′Leu and −2′Pro away from the channel axis. Binding of ivermectin to the gly-GlyR causes a clockwise inward rotation of the TMD. As a result, while the extracellular half of the pore undergoes little change, the intracellular entrance shrinks.