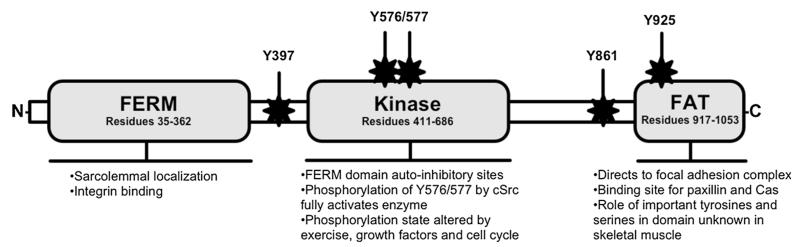
Fig. 1.
Simplified structure, domain roles and important phosphorylation sites of FAK. Autoinhibition is a result of interactions between the FERM and kinase domains, which prevents autophosphorylation of Y397, the major phosphorylation site of FAK. Phosphorylation of Y397 creates strong binding affinities for proteins containing SH2-domains, mainly cSrc and PI3K. Binding of cSrc induces phosphorylation of Y576/577, resulting in FAK’s full activation. In skeletal muscle, the role of major tyrosine and serines in the FAT and preceding linker domain remain unknown. Figure based on (Franchini 2012; Hanks et al. 2003; Lietha et al. 2007)