Figure 6.
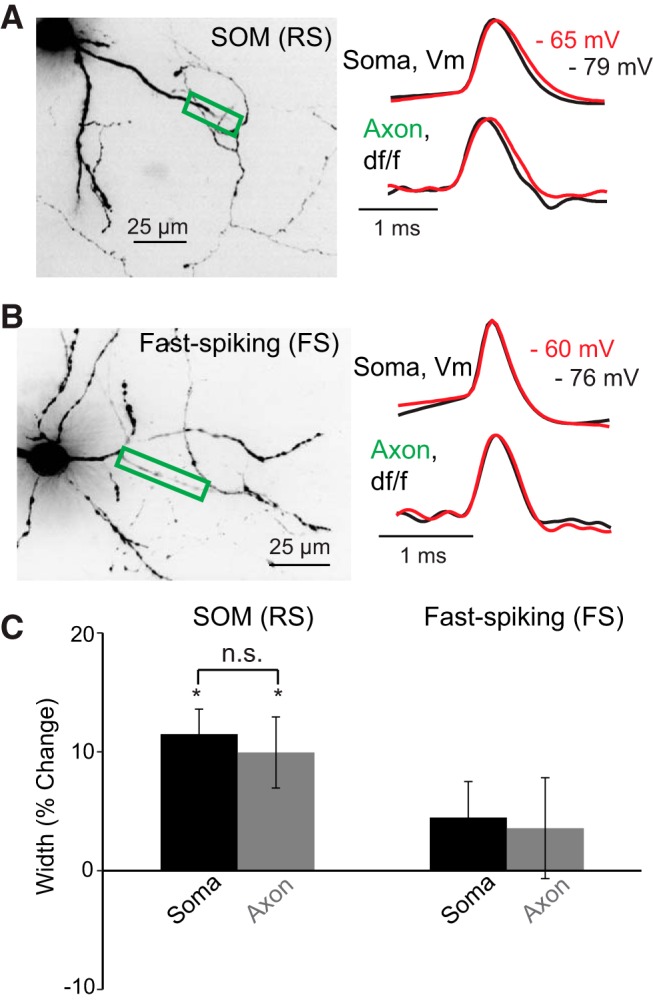
Subthreshold somatic depolarization significantly increases the duration of action potentials in SOM-expressing (RS) but not FS interneurons. A, B, Left, Confocal Z-projections of VSD-filled SOM (RS) and FS interneurons. Colored boxes represent regions of the axon imaged to assess action potential kinetics. A, B, Right, Average fluorescence traces [SOM (RS), 4 trial average; FS, 7 trial average], in response to somatically generated action potentials recorded optically in the axon or electrically at the soma at depolarized (red) or resting membrane potentials (black). C, Bar graphs represent the average percentage change in action potential duration at the soma and axon in response to subthreshold depolarization. Although depolarization of the soma causes a statistically significant increase in action potential duration in SOM somata and axons (*p < 0.05), there was no significant difference between these compartments (p > 0.05). Optical and electrical traces are normalized to peaks. n.s., Not significant.
