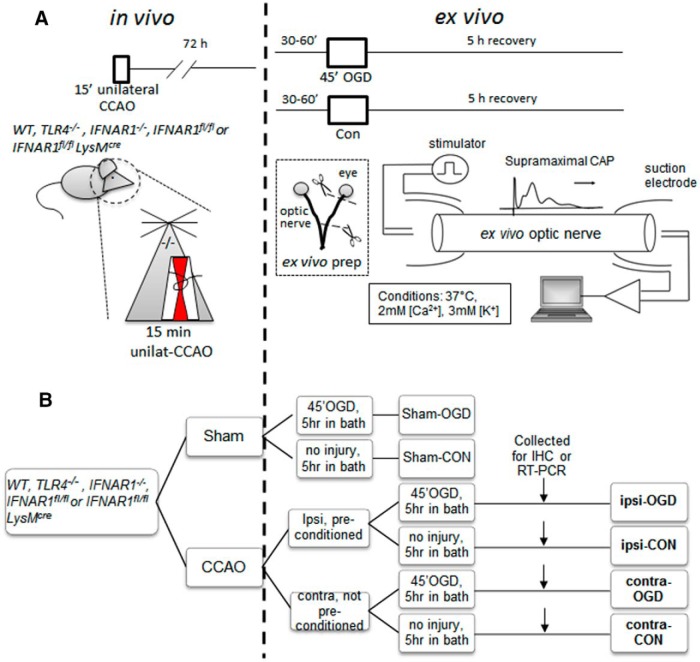
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram showing combined in vivo/ex vivo IPC experimental paradigm. WT, TLR4−/−, IFNAR1−/−, IFNAR1fl/fl, or IFNAR1fl/fl LysMcre 12- to 14-week-old male mice (all on C57BL/6 background) were subjected to either 15 min CCAO (our IPC pulse) or sham surgery. Seventy-two hours later, mice were killed by CO2 exposure and MONs were dissected out and placed in an interface perfusion chamber. Electrodes were put in place, and MONs were allowed to equilibrate in control conditions for 60 min, followed by 45 min exposure to OGD. Oxygen and glucose were then restored to baseline levels. CAPs were monitored before, during, and after OGD (for details, see Materials and Methods). After 5 h in normoxic/normoglycemic control (“recovery”) conditions, selected MONs were collected and processed for immunohistochemistry (A). The experimental groups are named in bold font according to the following: (1) position of the MON in question relative to CCAO surgery (i.e., ipsilateral or contralateral); (2) their initial in vivo exposure (i.e., sham surgery or CCAO); and (3) their subsequent ex vivo exposure [i.e., control (Con) or OGD] (B). IHC, Immunohistochemistry.