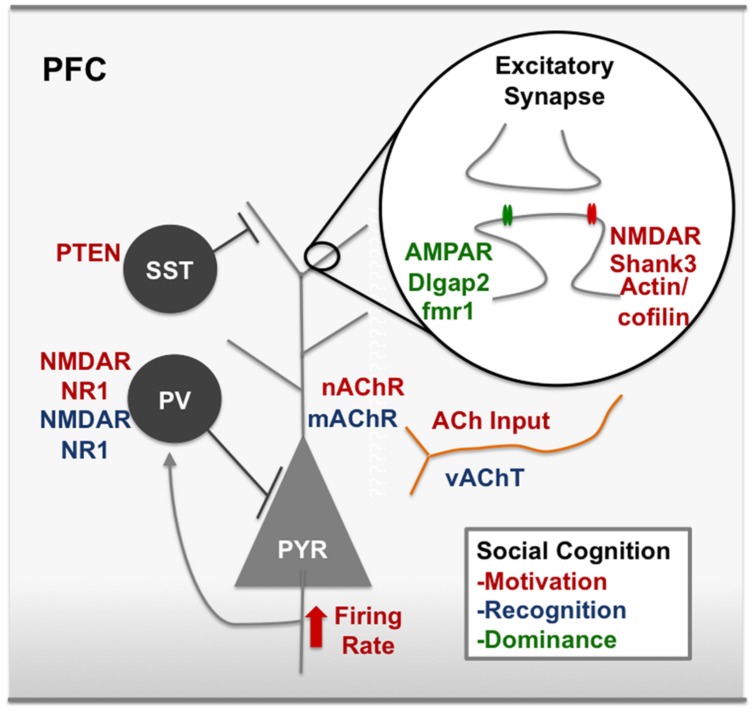
FIGURE 3.
Modulators of social cognition in the rodent PFC. Red text represents nodes of the circuit that, when disrupted, decrease social motivation. For example, synaptic scaffolding proteins on excitatory synapses like Shank3 and IRSp53 have been associated with social motivation in the PFC, as have cytoskeleton remodelers, actin and cofilin. NMDARs at excitatory synapses are also a key node of the social motivation circuit. ACh input to the PFC and nicotinic receptors have also been shown to modulate social motivation, however, it is unclear which cell types are important for ACh action or whether these effects are pre or post-synaptic. Blue text represents nodes of the circuit that, when disrupted, decrease social recognition. For example, disrupting gabaergic neurotransmission by removing the NR1 subunit on cortical gabaergic interneurons disrupts social recognition. Green text represents nodes of the circuit that are involved in dominance behavior. For example, bidirectional modulation of AMPARs and mutations in the fmr1 gene. ACh, acetylcholine; AMPAR, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor; dlgap2, disks large-associated protein 2, fmr1, fragile X mental retardation 1; IRSp53, insulin receptor substrate protein of 53 kDa, mAchR, muscarinic acetylcholine receptor, nAChR, nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, NMDAR, N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor, PV, parvalbumin postitive interneuron, vAChT, vesicular acetylcholine transporter. See text for references.