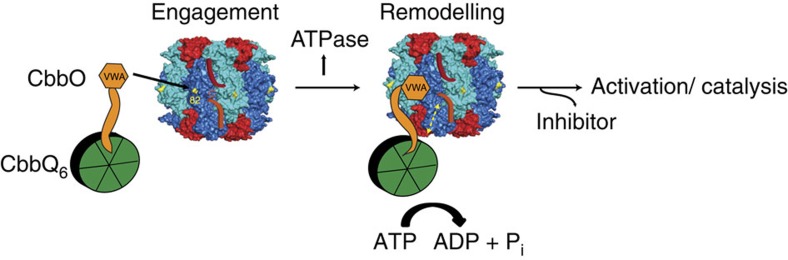
Figure 6. Proposed model of CbbQO function visualized using form I rubisco.
CbbQO binds to inhibited rubisco complexes via the acidic surface residue (Asp 82, coloured yellow) of the rubisco large subunit using the MIDAS binding site located on CbbO. The AAA+ hexamer formed by CbbQ may also interact with rubisco directly, possibly via the C terminus of the large subunit (indicated by yellow dashed double arrow). Productive binding, which involves both Asp 82 and the C terminus, results in a stimulation of ATPase activity. This provides the energy used to remodel the inhibited rubisco active site allowing release of the inhibitor. The CbbQO model is not drawn to scale. The form I rubisco model is from Halothiobacillus neapolitanus (pdb:1SVD).