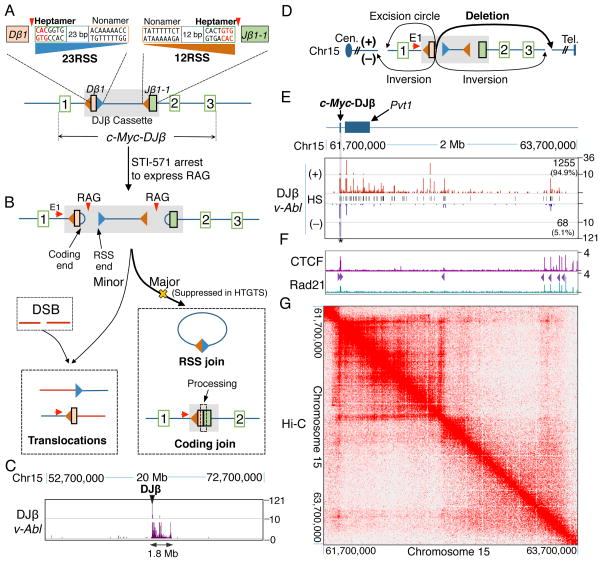
Figure 1. Abundant DSBs in the 1.8-Mb c-Myc-DJβ Loop Domain in v-Abl Pro-B Cells.
(A) Diagram of c-Myc-DJβ and sequences of Dβ1 23RSS (blue) and Jβ1-1 12RSS (orange). Red triangles indicate RAG cleavage-sites. (B) RAG-initiated DSBs in c-Myc-DJβ cassette participate in cassette DJβ rearrangements but rarely to translocations involving DSBs on other chromosomes. Red arrows indicate HTGTS primer positions. (C) Linear plot with a broken y axis showing HTGTS junction profiles in indicated 20-Mb region containing c-Myc-DJβ. (D) Potential junctional outcomes between bait Dβ1 23RSS coding ends and other DSBs in cis include deletions, excision circles, and inversions. (E) HTGTS junction profiles in v-Abl cells within indicated 2-Mb region containing c-Myc-DJβ. For all panels, unmarked ticks represent 0. Black lines in the middle show hotspot (HS) positions (listed in Table S1). Junction numbers and percentages in + or − orientation downstream of c-Myc-DJβ are shown. Cassette location is shadowed in gray. Star indicates a good cryptic RSS. (F) ChIP-seq profiles of CTCF and Rad21 in the 2-Mb region defined in (E). CBE orientation is indicated by purple triangles. (G) Heat map showing the 1.8-Mb c-Myc loop domain defined by in situ Hi-C data in CH12-LX cell line. See also Figure S1 and Table S1.