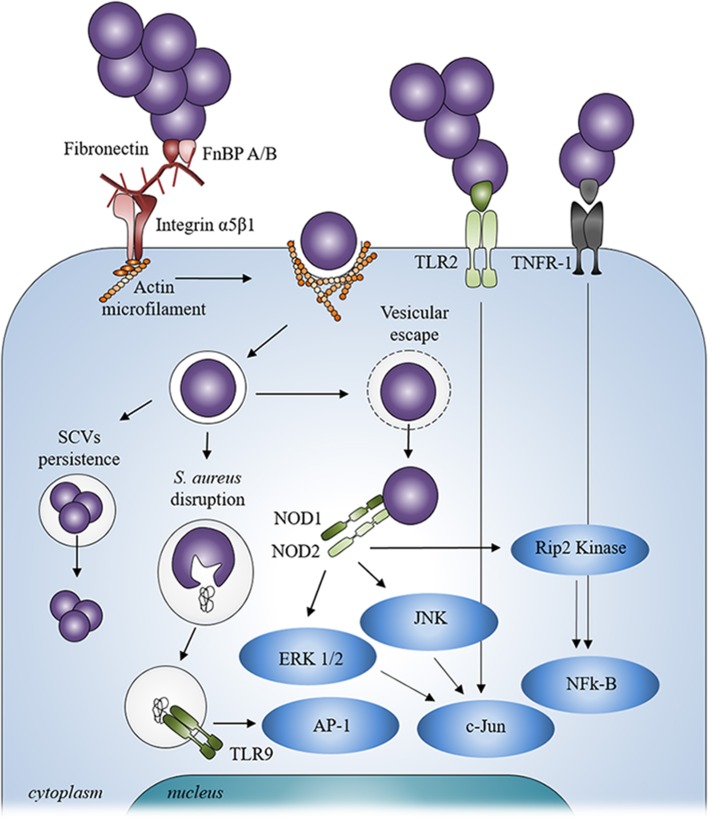
Figure 2.
Staphylococcus aureus signaling mechanism after contact and internalization by osteoblasts. After internalization, Staphylococcus aureus can escape from vesicle, be disrupted from inside the vesicle or persist inside osteoblasts through a SCV phenotype. Staphylococcus aureus can also interact with extracellular receptors TLR2 and TNFR-1 and with intracellular receptors TLR9 and NODs after its internalization into osteoblasts thanks to α5β1 integrin and actin filaments.