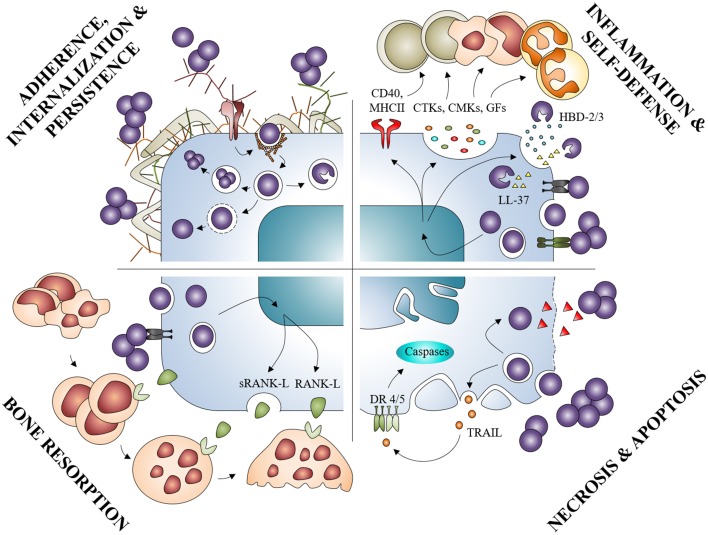
Figure 6.
Summary diagram of the osteoblasts responses in presence of Staphylococcus aureus. S. aureus can interact with osteoblasts and provoke: inflammation by increased release of mediators such as cytokines (CTKs), chemokines (CMKs), or growth factors (GFs); osteoblast self-defense by the production of AMPs (HBD-2/3, LL-37); osteoblasts death through apoptosis or necrosis; bone resorption by activation of the RANK/RANK-L complex.