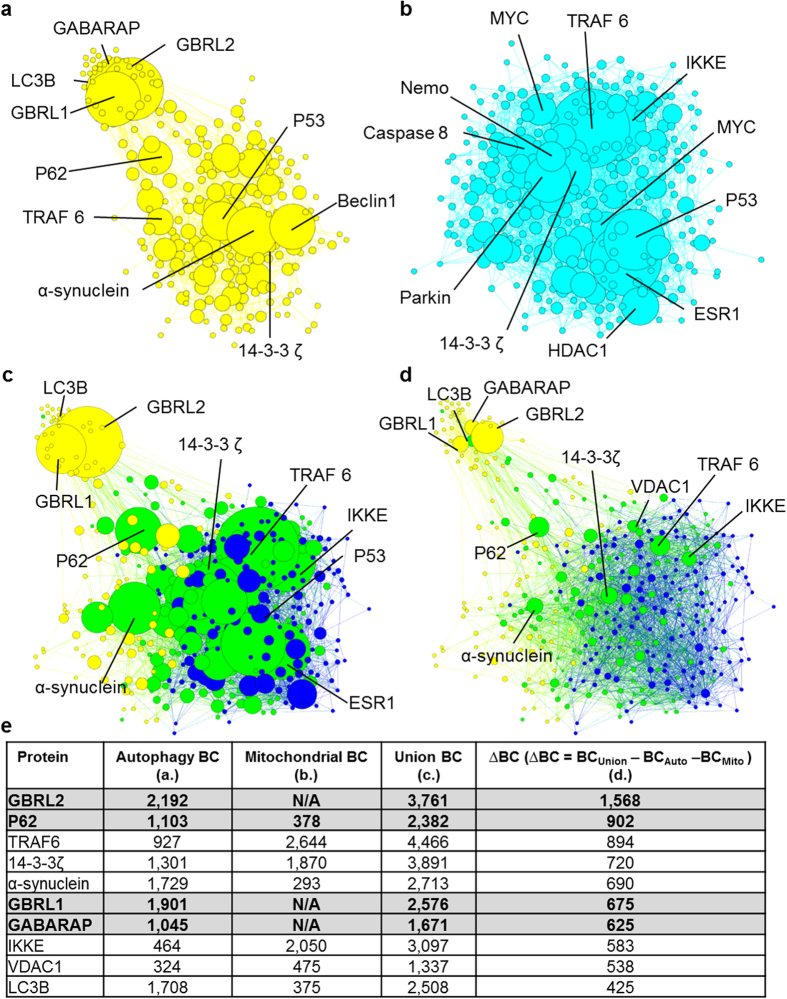
Figure 1. Protein-protein interaction networks identify candidate targets that modulate MPP+ toxicity.
(a,b) Protein-protein interaction networks representing mitochondrial dysfunction and the dysregulation of autophagy following MPP+ exposure were created. Seedlists of proteins with validated roles in either (a) autophagy (yellow) or (b) mitochondrial dysfunction (cyan/blue) were used to sample iRef Index. Nodes are sized according to betweenness centrality (BC) with the ten nodes with the highest value of BC labelled. (c,d) A union network representing cross talk between mitochondrial dysfunction and autophagy was formed. Nodes which are common to both networks are coloured green and size represents overall BC in the union network (c), or ΔBC (BCUnion − BCAuto − BCMito) (d) to represent the importance of each node in linking these two processes together. (e) Targets for in vitro validation were selected. BC values for the 10 nodes with highest ΔBC as represented in each of the four networks – highlighted proteins were investigated experimentally and N/A indicates that the node does not appear in the sub-network and therefore has no BC.