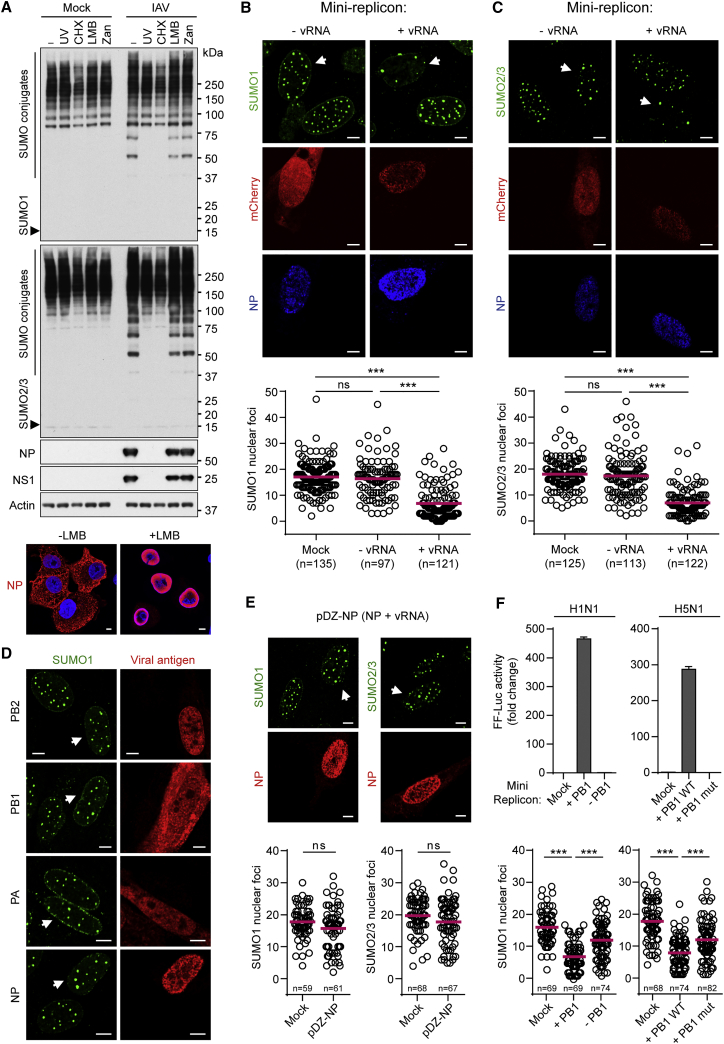
Figure 2.
IAV Polymerase Activity Contributes to SUMO Remodeling
(A) Western blot of lysates from IAV-infected A549 cells treated with different inhibitors. Cells were infected with IAV or UV-inactivated IAV (UV) at 5 PFU/cell, followed by incubation with 50 μg/ml cycloheximide (CHX), 11 nM leptomycin B (LMB), or 10 μM zanamivir (Zan) for 12 hr. SUMO1, SUMO2/3, NS1, NP, and actin were detected. (Bottom) Immunofluorescence shows NP staining at 12 hr post-infection in A549s ± LMB. DAPI was used to stain DNA.
(B and C) Immunofluorescent analyses of MRC5s transiently expressing PB1, PB2, PA, NP, and a negative-sense viral-like mini-replicon mCherry reporter construct (+vRNA), or PB1, PB2, PA, NP, and mCherry (no viral-like reporter; −vRNA).
(D) Immunofluorescent analysis of MRC5s individually expressing PB1, PB2, PA, or NP.
(E) Immunofluorescent analysis of MRC5s transiently transfected with pDZ-NP, which expresses both NP protein from a pol-II promoter and NP vRNA from a pol-I promoter.
(F) (Top) Luciferase-based mini-replicon assays in 293Ts to assess polymerase activity. (Left) (WSN, H1N1) Cells transiently expressing PB1 (or not), PB2, PA, NP, and a negative-sense viral-like mini-replicon Firefly luciferase reporter construct. (Right) (KAN-1, H5N1) Cells transiently expressing PB1 (or an E445A/E446A inactive mutant), AvianPr-PB2-E627K, PA, NP, and a negative-sense viral-like mini-replicon Firefly luciferase reporter construct. Bars represent mean values from triplicates (±SD). (Bottom) Quantification of SUMO1 nuclear foci for the conditions indicated above as determined by the mCherry-based mini-replicon reporter assay in MRC5s. For (B)–(F), cells were transfected for 36 hr prior to processing or fixation and immunostaining. Representative images are shown. Scale bars represent 5 μm. Statistical significance in panels (B), (C), (E), and (F) was determined using the Student’s t test (∗∗∗p < 0.0001; ns, non-significant). See also Figure S2.