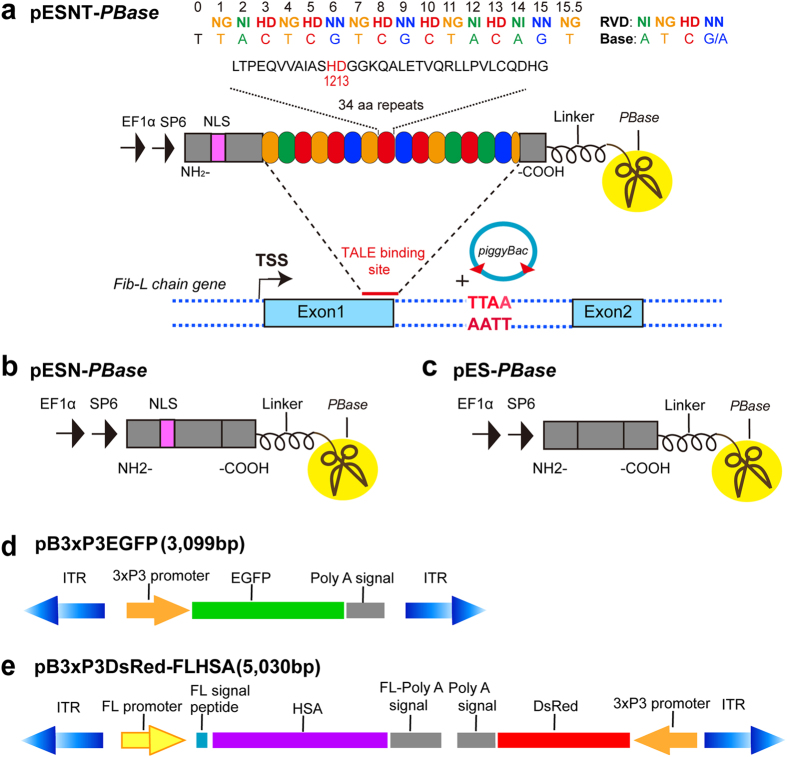
Figure 1. Design and construction of artificial TALE and PB transposon plasmids for producing transgenic silkworms.
(a) Schematic representation of the TALE tandem repeat domain and each repeat monomer, including the two repeat variable di-residues (RVD) at positions 12 and 13 of each amino acid sequence, which determine the base recognition specificity. TALE arrays comprising 16 repeats (colored ovals) fused to the PB transposase (PBase). EF1α, elongation factor-1 alpha promoter; SP6, a prokaryotic promoter used for high-efficiency mRNA transcription in vitro; NLS, nuclear localization signal; Fib-L gene, fibroin light-chain gene of silkworm; TSS, transcriptional start site; TTAA, the target insertion site of the PB transposon. (b) Schematic representation of the TALE repeats are deleted in the pESN-PBase plasmid based on the pESNT-PBase plasmid. (c) Both the TALE repeat and the NLS are deleted in the pES-PBase plasmid. (d,e) Diagram of the structure of PB transposon plasmids. ITR, inverted terminal repeats of the PB transposon; 3 × P3 promoter, an artificial promoter specifically driving reporter gene expression in the ocelli of larvae or compound eyes of moths; FL promoter, silkworm fibroin light-chain promoter; HSA, human serum albumin.