Figure 3.
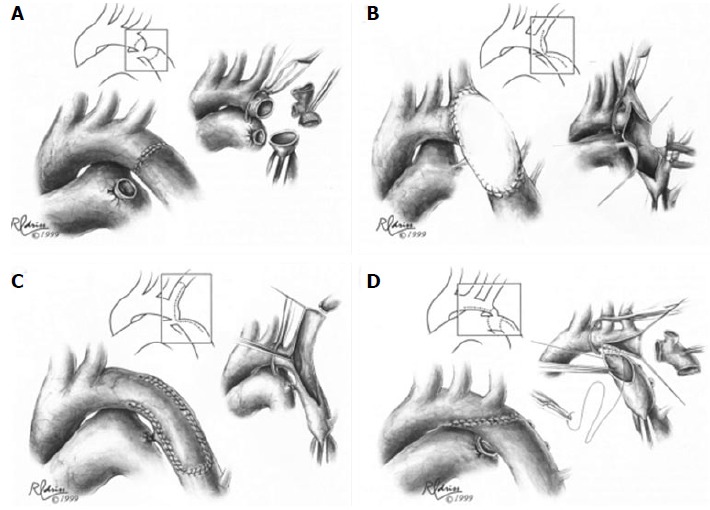
Surgical techniques in coarctation repair. A: Resection and simple end-to-end anastomosis. The coarctation is resected, and an end-to-end, circumferential anastomosis is created; B: Patch aortoplasty. An incision is extended across the coarctation, and a patch is sutured in place to enlarge the stenotic region; C: Subclavian flap aortoplasty. The left subclavian artery is ligated and divided. A longitudinal incision is extended from the proximal left subclavian artery beyond the area of coarctation, and the proximal left subclavian stump is folded down to enlarge the area of coarctation; D: Resection with extended end-to-end anastomosis. The coarctation is resected using a broad, longitudinal incision, and an oblique anastomosis is constructed between the undersurface of the transverse arch and the descending thoracic aorta. Figures adapted and reprinted with permission from the Journal of Cardiac Surgery[30].
