Figure 1.
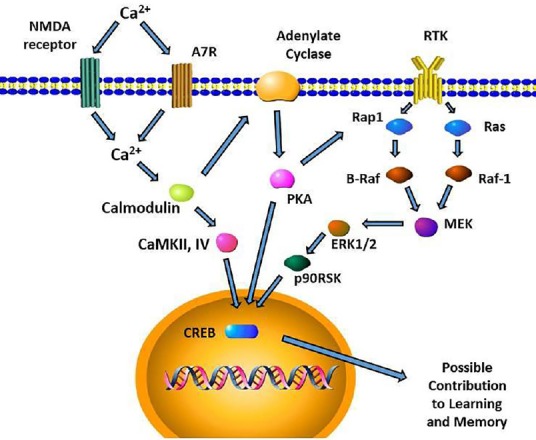
Postsynaptic functions of α7 nAChR in the hippocampus.
Intracellular signaling cascades leading to CREB activation for long term memory formation are depicted. Presynaptic glutamate release as well as α7 nAChR activation will increase Ca2+ influx. This increase in Ca2+ leads to activation of ERK, CaMKII/IV, and PKA which all leads to CREB activity. Though activation of ERK can be triggered by the activity of growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), PKA can activate ERK via RAP1. Intracellular Ca2+ can also activate protein kinase C (PKC) which in turn activates Ras/Raf-1 cascade. PKA activity is also known to activate Raf-1 in SH-SY5Y cells. The activation of α7 nAChR subsequently may contribute to enhancement of learning and memory, among numerous other biochemical pathways that modulates it.
α7 nAChR: α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors; CaMKII/IV: calmodulin regulated kinases II/IV; CREB: cAMP response element-binding protein; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MEK: Methyl ethyl ketone; NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartate; PKA: protein kinase A; RAF: rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma; Rap1: Ras-proximate-1; p90RSK: p90 ribosomal S6 kinase.
