Figure 3.
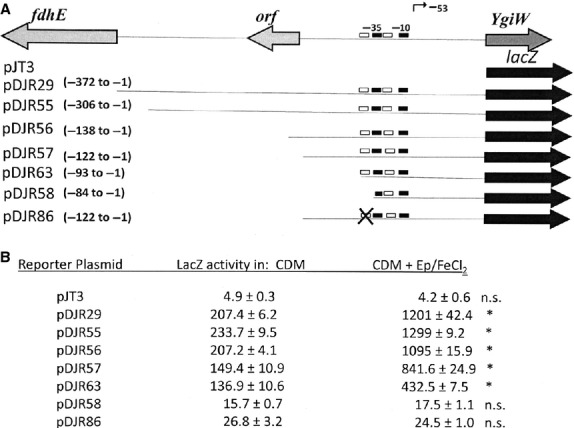
Catecholamine/iron-dependent induction of ygiW-qseBC requires a functional QseB binding site. (A) Schematic diagram of the ygiW-qseBC promoter region and transcriptional fusion constructs pDJR29, pDJR55, pDJR56, pDJR57, pDJR63, pDJR58, pDJR85 and pDJR86 (Juárez-Rodríguez et al., 2013b, 2014) showing the binding regions for QseB (white boxes), the –10 and –35 promoter elements (black boxes) and the primary transcriptional start site (bent arrow). Site-specific mutations in the QseB binding site are indicated with the × symbol. The numbering of the nucleotides is relative to the ygiW translational start codon. (B) β-galactosidase activity in A. actinomycetemcomitans 652 transformed individually with each reporter plasmid. Cultures were grown in chemically defined medium (CDM) or CDM supplemented with epinephrine (Ep; 50 μm) and FeCl2 (100 μm) and β-galactosidase activity was determined after 24 h of growth. Values are means of results from three independent experiments ± standard deviations. Statistical analysis was performed by using one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's multiple-comparison test. Significant differences (P < 0.05) are indicated by asterisks; n.s., not significant.
