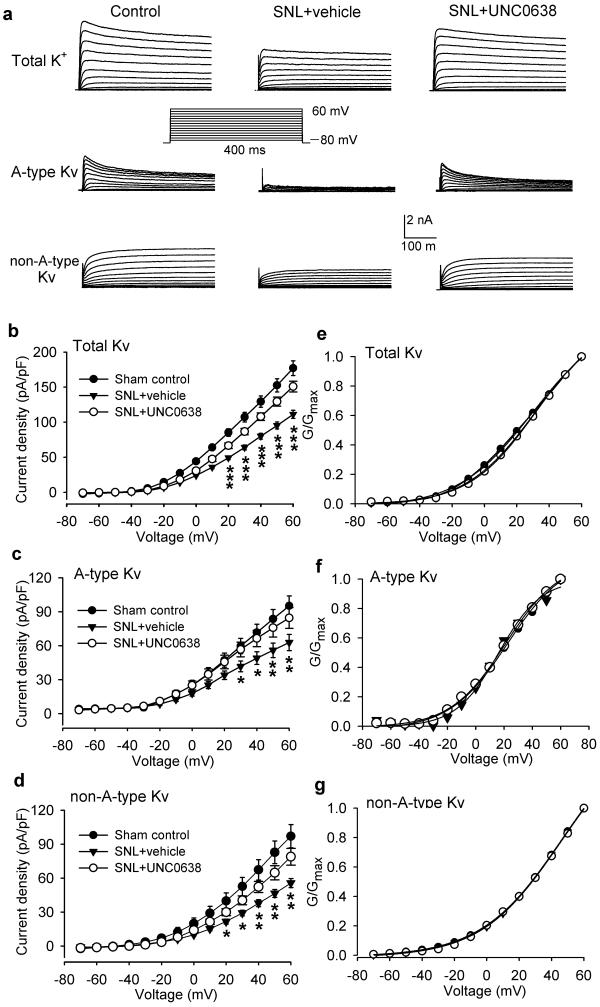
Figure 5. Inhibition of G9a activity restores Kv channel currents in DRG neurons reduced by nerve injury.
(a) Original traces of total whole-cell Kv currents, A-type Kv currents, and non-A-type Kv currents in DRG neurons from sham control rats, SNL rats treated with vehicle, and SNL rats treated with UNC0638. Neurons were held at −80 mV and depolarized from −70 to 60 mV in 10-mV increments (inset). (b-d) Current densities of total whole-cell Kv currents (b, n = 21 neurons in each group, n = 5 rats in each group), A-type Kv currents (c, n = 16 neurons in each group, n = 5 rats in each group), and non-A-type Kv currents (d, n = 16 neurons in each group, n = 5 rats in each group) in DRG neurons dissociated from control rats, SNL rats treated with vehicle and SNL rats treated with UNC0638. (e-g) The conductance–voltage (G–V) curves of total and A-type Kv currents in DRG neurons from control and SNL rats treated with UNC0638 or vehicle. The V0.5 values of total Kv currents (control, 31.1 ± 1.7 mV; SNL+vehicle, 33.0 ± 1.0 mV; SNL+UNC0638, 32.5 ± 1.2 mV), A-type Kv currents (control, 19.7 ± 3.2 mV; SNL+vehicle, 16.0 ± 5.3 mV; SNL+UNC0638, 16.8 ± 4.3 mV) and non-A-type Kv currents (control, 46.4 ± 1.3 mV; SNL+vehicle, 45.2 ± 1.0 mV; SNL+UNC0638, 45.9 ± 3.2 mV) were not significantly different between the three groups. There was no significant difference in the k value of total Kv currents (control, 24.6 ± 1.1 mV; SNL+vehicle, 22.3 ± 0.6 mV; SNL+UNC0638, 21.1 ± 0.8 mV), A-type Kv currents (control, 19.6 ± 1.9 mV; SNL+vehicle, 13.7 ± 1.3 mV; SNL+UNC0638, 15.1 ± 1.5 mV) and non-A-type Kv currents (control, 25.0 ± 0.5 mV; SNL+vehicle, 24.3 ± 0.4 mV; SNL+UNC0638, 24.7 ± 1.3 mV) between the three groups. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, compared with the corresponding value in the control group (two-way ANOVA).