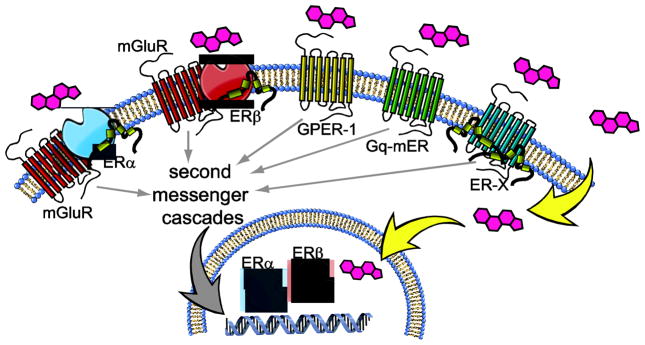
Figure 2.
Estrogens act through a diverse set of receptor subtypes. The ERα and ERβ subtypes are found in the nucleus of the cell, where they respond to estrogens to alter gene expression. After posttranslational modification, both ERα and ERβ are found associated with the plasma membrane, where they form a complex that includes caveolin and mGluR subtypes. Estrogens can also act at membrane-associated GPER-1, Gq-mER, and ER-X receptor subtypes, the latter of which is found embedded in caveolar-like microdomains. The membrane-associated receptors are able to exert rapid effects by interactions with ion channels, and slower effects through second messenger cascades that affect transcription.