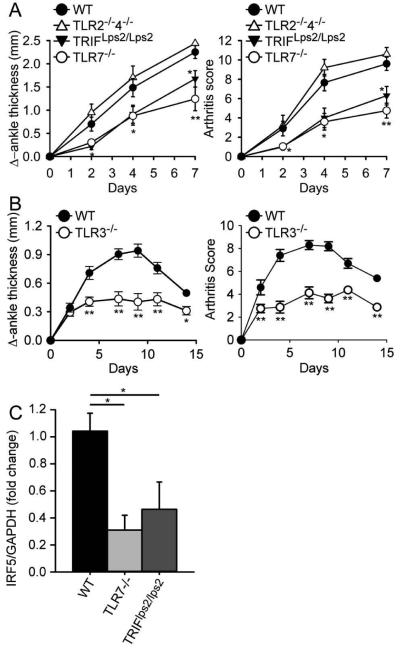
Figure 3.
TLR7-deficient ,TRIF-mutant and TLR3-deficient mice develop less severe arthritis following transfer of K/BxN serum. (A) C57BL/6 wildtype (WT; n = 10), TLR7-deficient (TLR7−/−; n = 10), TRIF-mutant (TRIFLps2/Lps2; n = 10), and TLR2 and 4 double-deficient (TLR2−/−4−/−; n = 5) mice were injected i.p with 150 μl of K/BxN serum on day 0 and day 2. Change in ankle thickness (left) and clinical score (right) were measured on days 0, 2, 4 and 7. (B) C57BL/6 wildtype (WT; n = 10) and TLR3-deficient (TLR3−/−; n =8) mice were injected i.p with 75 μl of K/BxN serum on day 0. Change in ankle thickness (left) and clinical score (right) were measured on days 0, 2, 4, 7, 9, 11 and 14. (C) IRF5 expression levels were measured by RT-PCR in wrist joints isolated 7 days after K/BxN serum administration from C57BL/6 wildtype (WT; n = 4), TLR7-deficient (TLR7−/−; n = 5) and TRIF-mutant (TRIFLps2/Lps2; n = 5) mice described in (A). * = P < 0.05; ** = P < 0.01; *** = P < 0. 001 versus WT.