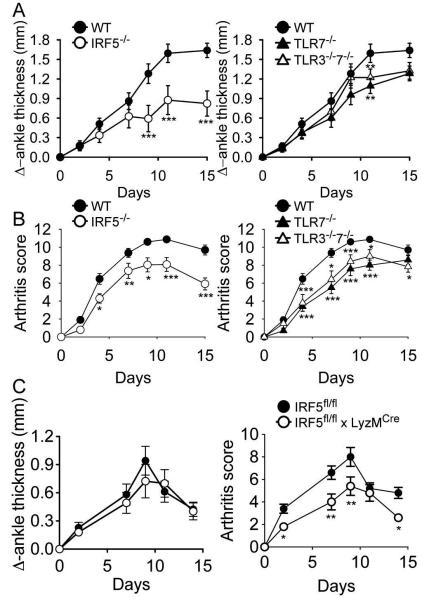
Figure 5.
Mice deficient in IRF5 or TLR7 develop less severe arthritis but no additional protection is seen in mice deficient in both TLR7 and TLR3. C57BL/6 wildtype (WT; n = 20), IRF5-deficient (IRF5−/−; n = 12), TLR7-deficient (TLR7−/−; n = 13), and TLR3 and 7 double-deficient (TLR3−/−7−/−; n = 12) mice were injected i.p with 150 μl of K/BxN serum on day 0 and day 2. Change in ankle thickness (A) and clinical score (B) were measured on days 0, 2, 4, 7, 9, 11 and 15. The IRF5−/− data are shown in the left hand panels and the TLR7−/− and TLR3−/−7−/− data are shown in the right hand panels for clarity. There were no statistically significant differences between the IRF5−/−, TLR7−/− and the TLR3−/−7−/− cohorts except for day 15 where the change in ankle thickness and clinical score were lower in the IRF5−/− cohort than in the other 2 cohorts (P < 0.05). (C) IRF5flox/flox mice (wild-type; n = 5) and LyzMcre IRF5flox/flox mice (n = 5) were injected i.p with 75 μl of K/BxN serum on day 0. * = P < 0.05; ** = P < 0.01; *** = P < 0. 001 versus WT.