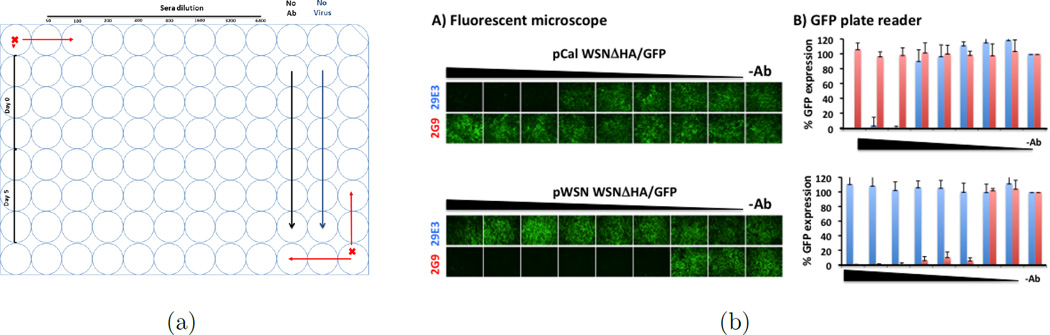
Figure 1.
(a) Typical design; (b) Identity of pCal WSNΔHA/GFP: Influenza A/California/04/09 HA-pseudotyped WSN-GP/GFP virus (pCal WSNΔHA/GFP, top) was tested in the GFP-based microneutralization assay using the influenza A/California/04/09 monoclonal neutralizing antibody 29E3 (blue). Influenza A/WSN/33 monoclonal neutralizing antibody 2G9 (red) was used as an internal control. Two-fold serial dilutions of the antibodies (starting concentration of 100 ng) were pre-incubated with the pCalE3 WSNΔHA/GFP virus for 1 hour. The antibody-virus mixture was used to infect MDCK HA-expressing cells. Virus infection was monitored under a fluorescent microscope (a) and GFP-expression was quantified under a GFP plate reader (b). Percentage of GFP expression is illustrated for the different antibody dilutions. Virus in the absence of antibody (−Ab) was used to set up 100% GFP expression. Same monoclonal antibodies were also tested with the influenza A/WSN/33 HA-pseudotyped WSNΔHA/GFP virus (pWSN WSNΔHA/GFP, bottom). As expected, monoclonal antibody 29E3 specifically neutralize the pCal WSNΔHA/GFP virus but not pWSN WSNΔHA/GFP. To the contrary, monoclonal antibody 2G9 neutralized the pWSN WSNΔHA/GFP but not the pCalE3 WSNΔHA/GFP virus.