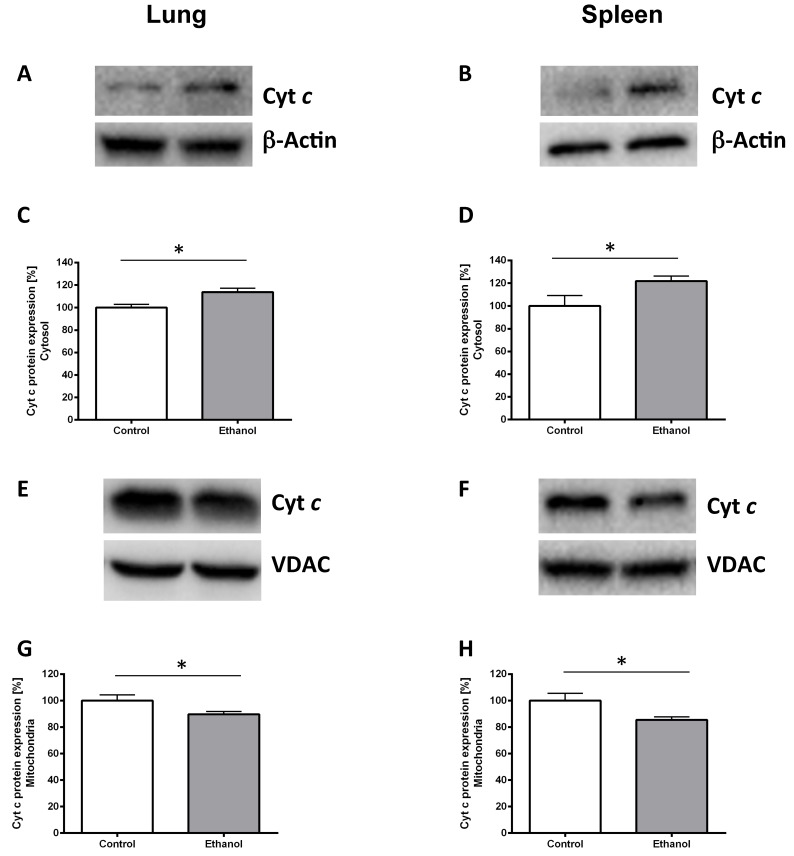
Figure 2.
Chronic alcohol consumption increases cytochrome c release out of the mitochondria. Cytosolic and mitochondrial extracts of lung and spleen samples were separated by SDS-PAGE, the expression of cytochrome c was detected by immunoblotting. Representative Western blot of cytosolic cytochrome c expression of a pair of ethanol treated and control rats (2A: lung, 2B: spleen). Dose-response curves (2C: lung, 2D: spleen). Results are mean ± SEM (n=8-10). *P < 0.05 represents the difference between chronic alcohol consumption and control groups. Chronic alcohol consumption resulted in increased cytochrome c release out of the mitochondria. Representative Western blot of mitochondrial cytochrome c protein expression of a pair of ethanol treated and control rats (2E: lung, 2F: spleen). Dose response curves (2G: lung, 2H: spleen). Results are mean ± SEM (n=8-10). *P < 0.05 represents the difference between chronic alcohol consumption and control groups. Chronic alcohol consumption resulted in a decreased mitochondrial cytochrome c amount. The experiments were repeated and similar results were obtained. VDAC or β-actin served as a control for equal protein loading.